一、前言
大家在开发中,最让人头疼的就是:对象之间的拷贝,前端的VO和数据库的Entity不一致!
性能最好的就是手动set,主要是枯燥且无技术含量,不仅耗费大量时间而且很容易出错;
所以我们要成为优秀的程序员,要多借助轮子,开发效率事半功倍,开发技能也是增长不少!
如果系统性能没有要求,怎么实现都是好的,但是我们要有追求哈,追求高质量!
每个东西都有存在的价值,不要捧一踩一哈!
二、MapStruct简介
MapStruct是基于JSR 269的Java注释处理器,用于生成类型安全的 Bean 映射类。
您所要做的就是定义一个映射器接口,该接口声明任何所需的映射方法。在编译过程中,MapStruct将生成此接口的实现。此实现使用纯 Java 方法调用在源对象和目标对象之间进行映射,即无反射或类似内容。
与手动编写映射代码相比,MapStruct通过生成繁琐且容易出错的代码来节省时间。遵循配置方法的约定,MapStruct使用合理的默认值,但在配置或实现特殊行为时会步入歧途。
三、优势
与动态映射框架相比,MapStruct具有以下优点:
- 通过使用普通方法调用而不是反射快速执行。
- 编译时类型安全:只能映射彼此映射的对象和属性,不会意外地将订单实体映射到客户 DTO 等。
- 在构建时清除错误报告,如果
- 映射不完整(并非所有目标属性都已映射)
- 映射不正确(找不到正确的映射方法或类型转换)
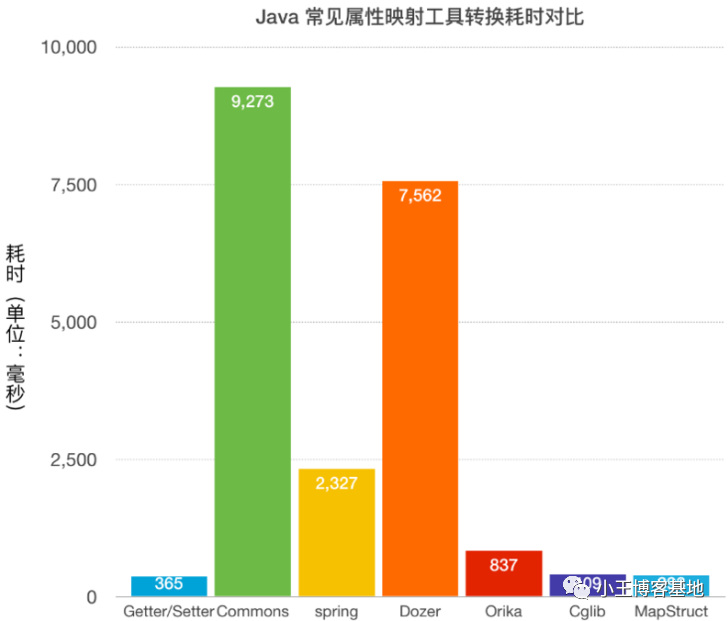
性能图大家可以看一下:
四、整合实战
1、使用
@Mapper将接口标记为映射接口对于源对象和目标对象中具有不同名称的属性,可以使用注释来配置名称:@Mapping按照约定,接口声明一个成员Mappers INSTANCE,为客户端提供对映射器实现的访问。下面我们来具体使用!
2、. 导入依赖
这里使用最新的,如果引入了lombok可能会有问题,就是他们俩都是在编译期运行的,mapstruct如果比lombok先执行,就会找不到get、set方法,所以会有问题,官网已经有了解决方案!现在是启动不会报错!
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
</dependency>
3、错误总结
- 不会自动生成impl实现类?
我们需要加上依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
- 重新启动就会出现和lombok的冲突问题:
java: No property named "name" exists in source parameter(s).
Type "UserVO" has no properties.
官网解决文章地址:https://mapstruct.org/faq/#Can-I-use-MapStruct-together-with-Project-Lombok。
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>1.5.3.Final</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok-mapstruct-binding</artifactId>
<version>0.2.0</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
4、常用实战一
用户表:
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Integer age;
}
前端用户VO:
@Data
public class UserVO {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
我们创建接口进行两个对象之间的映射:
import com.example.demo.mapstruct.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.mapstruct.entity.UserVO;
import org.mapstruct.Mapper;
import org.mapstruct.Mapping;
import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers;
/**
* @author wangzhenjun
* @date 2023/1/28 16:05
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
UserMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
@Mapping(source ="name",target = "username")
User userVOToUser(UserVO userVO);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
属性多了可以嵌套:
@Mappings({
@Mapping(source ="name",target = "username"),
@Mapping(source ="name1",target = "username1")
})
也可以:
@Mapping(source ="name",target = "username")
@Mapping(source ="name1",target = "username1")
编写测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Test
void demoMapstruct(){
UserVO userVO = new UserVO(1,"小红",18);
User user = UserMapper.INSTANCE.userVOToUser(userVO);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
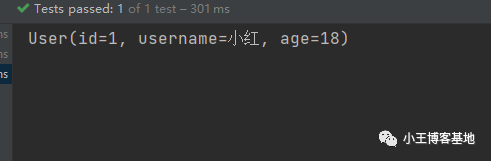
我们看到拷贝没有任何问题!
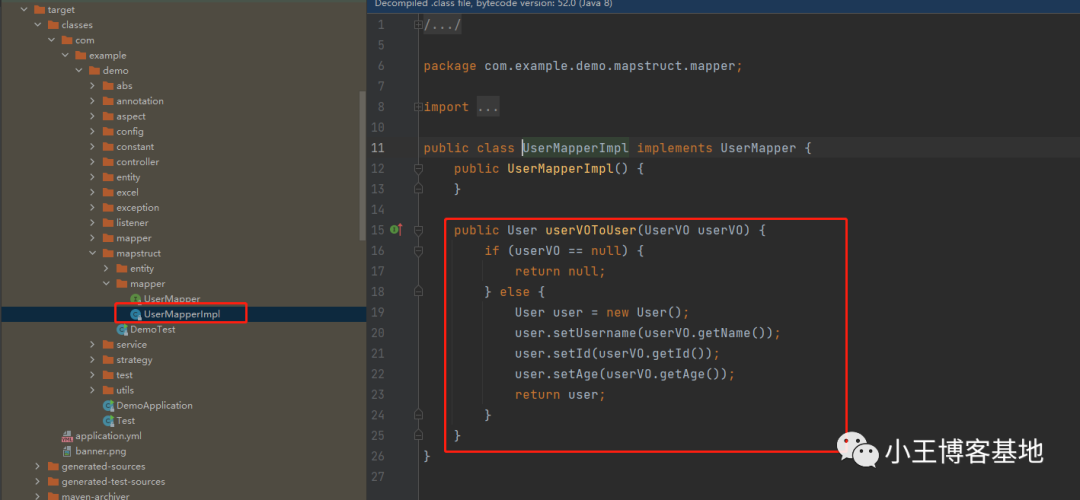
我们看看是怎么实现的:
mapstruct会在编译期自动生成实现类去帮助我们去赋值,不指定默认策略,名称一致进行copy!不一致可以按上面的进行指定,不指定则不会有set方法!
5、常用实战二
下面进行多个源参数的映射方法演示:
我们把user类加上一个字段:
private BigDecimal score;
新增加一个Score类:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Score {
private Integer studentId;
private BigDecimal score;
}
调整上面的UserMapper接口:
@Mappings({
@Mapping(source ="userVO.name",target = "username"),
@Mapping(source ="score.score",target = "score")
})
User userVOToUser(UserVO userVO, Score score);
测试代码:
UserVO userVO = new UserVO(1,"小红",18);
Score score = new Score(1,new BigDecimal(100));
User user = UserMapper.INSTANCE.userVOToUser(userVO,score);
System.out.println(user);
结果显示正常:

6、常用实战三
我们在来看一个企业级能够用得上的,就是自定义方法,然后进行赋值:
场景:一个商品有长宽高,我们把长宽高从cm变为m!
还有很多String转Integer、Float等等,都是按照下面这种自定义方法去实现!
VO和对象都是一样的哈!
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ProductVO {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal length;
private BigDecimal width;
private BigDecimal high;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
看清楚,别导错包了!
qualifiedByName:指定自定义方法的名称。
@Named("cmToM"):起别名,不使用找不到方法。
可以写一起,也可以整一个工具类里写方法,在这里进行引用!如果是使用spring,我们可以把接口作为bean进行注入调用(推荐)加上参数即可开启:
@Mapper(componentModel = MappingConstants.ComponentModel.SPRING)
/**
* @author wangzhenjun
* @date 2023/1/28 17:13
*/
@Mapper(componentModel = MappingConstants.ComponentModel.SPRING)
public interface ProductMapper {
@Mapping(source = "length",target = "length",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
@Mapping(source = "width",target = "width",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
@Mapping(source = "high",target = "high",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
Product productVOToPrduct(ProductVO productVO);
@Named("cmToM")
default BigDecimal cmToM (BigDecimal oldValue){
if (oldValue == null) {
return BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
return oldValue.divide(new BigDecimal("100"));
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
测试:
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ProductMapper productMapper;
@Test
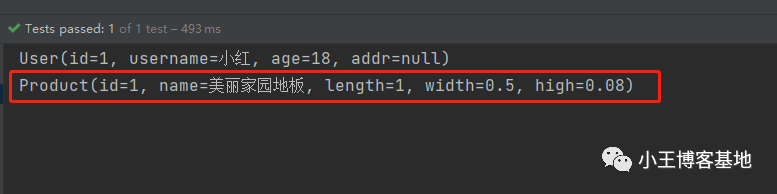
void demoMapstruct(){
ProductVO productVO = new ProductVO(1,"美丽家园地板",new BigDecimal(100),new BigDecimal(50),new BigDecimal(8));
Product product = productMapper.productVOToProduct(productVO);
System.out.println(product);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
完美转化!
7、常用实战四
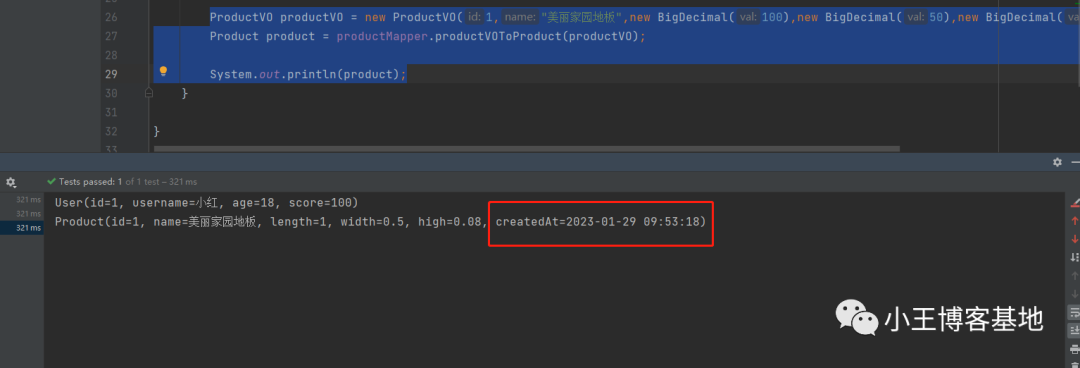
在实战一个LocalDateTime、String相互转化的,后面大家可以去官网文档去找你需要的:
在刚刚的商品类加个字段:
private String createdAt;
VO里也加上一个:
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
编写个转化类:
这里交给spring管理了,因为ProductMapper也交给spring管理,不加的话会找不到此类!
@Component
public class LocalDateTimeMapper {
public String asString(LocalDateTime date) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return date != null ? date.format(formatter): null;
}
public LocalDateTime asLocalDateTime(String date) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return date != null ? LocalDateTime.parse(date,formatter) : null;
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
ProductMapper修改一下:
uses = LocalDateTimeMapper.class使用咱们上面写的类即可!
@Mapper(componentModel = MappingConstants.ComponentModel.SPRING,uses = LocalDateTimeMapper.class)
public interface ProductMapper {
@Mapping(source = "length",target = "length",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
@Mapping(source = "width",target = "width",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
@Mapping(source = "high",target = "high",qualifiedByName = "cmToM")
Product productVOToProduct(ProductVO productVO);
@Named("cmToM")
default BigDecimal cmToM (BigDecimal oldValue){
if (oldValue == null) {
return BigDecimal.ZERO;
}
return oldValue.divide(new BigDecimal("100"));
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
测试一下:
ProductVO productVO = new ProductVO(1,"美丽家园地板",
new BigDecimal(100),new BigDecimal(50),
new BigDecimal(8), LocalDateTime.now());
Product product = productMapper.productVOToProduct(productVO);
System.out.println(product);
完美转化: