🍎 博客主页:🌙@披星戴月的贾维斯
🍎 欢迎关注:👍点赞🍃收藏🔥留言
🍇系列专栏:🌙 蓝桥杯
🌙我与杀戮之中绽放,亦如黎明的花朵🌙
🍉一起加油,去追寻、去成为更好的自己!
蓝桥杯倒计时 43天
文章目录
- 🍎、二分
- 🍎、例题分析
- 🍇、(AcWing)数的范围
- 🍇、(AcWing)四平方和
- 🍇、(AcWing)分巧克力
- 🍇、(AcWing)我在哪?
- 🍎、总结
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
🍎、二分
🍉、二分的简单定义
二分法(Bisection method) 即一分为二的方法. 设[a,b]为R的闭区间. 逐次二分法就是造出如下的区间序列([an,bn]):a0=a,b0=b,且对任一自然数n,[an+1,bn+1]或者等于[an,cn],或者等于[cn,bn],其中cn表示[an,bn]的中点.
🍉、二分的基本逻辑
算法:当数据量很大适宜采用该方法。采用二分法查找时,数据需是排好序的。
基本思想:假设数据是按升序排序的,对于给定值key,从序列的中间位置k开始比较,
如果当前位置arr[k]值等于key,则查找成功;
若key小于当前位置值arr[k],则在数列的前半段中查找,arr[low,mid-1];
若key大于当前位置值arr[k],则在数列的后半段中继续查找arr[mid+1,high],
直到找到为止,时间复杂度:O(log(n)) 。(来源百度百科)
🍉、二分的算法模板(y总)
//查找左边界 SearchLeft 简写SL
int SL(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
//查找右边界 SearchRight 简写SR
int SR(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1; //需要+1 防止死循环
if (check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return r;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
🔥博主对于在做题时该选择哪种模板时的看法:
首先我们在考虑使用哪个模板时,其实就是考虑mid, R,和 L的取值,我们肯定要先分析题目的意思,如果我们的答案在mid的右边,那么我们优先使用枚举区间右端点的模板,也就是选择mid = l + r + 1 >> 1往上取整的模板,同理,我们如果要的答案在mid的左边,择选择第一种mid = l + r >> 1的模板。还有,我们在考虑这道题能不能使用二分时,其实对于这道题是否具有单调性并不看重,如果具有二段性,就能使用二分。
🔥二分的几个应用场景
1:找大于等于数的第一个位置 (满足某个条件的第一个数)
2:找小于等于数的最后一个数 (满足某个条件的最后一个数)
3.查找最大值 (满足该边界的右边界)、
4.查找最小值 (满足该边界的左边界)
🍎、例题分析
🍇、(AcWing)数的范围
本题链接: 数的范围

简单分析题意:先输入一个长度为n的数组,然后进行q次询问,每次询问如果这个数组存在值=x,就把这个值在x的起始位置和终止位置返回,若不存在就输出 -1 -1;
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int s[N];
int n, q;
int main ()
{
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> s[i];
while(q --)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while(l < r)//枚举左端点
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(s[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
if(s[r] == x)
{
cout << r << " ";
l = 0, r = n - 1;
while(l < r)//z枚举右端点
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;//此时mid在右区间, mid要向上取整,所以要+1
if(s[mid] <= x) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
}
else cout << "-1 -1" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
🍇、(AcWing)四平方和
本题链接: 四平方和

简单分析题意: 由于 5 * 10^6的数据范围,所以不能枚举四个数,只能枚举两个数,把时间复杂度降到nlogn左右。

#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5000010;
int n;
int h[N], m[N];
int main ()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1,sizeof h ); //把h数组内的值全初始化为-1,标记为未用过
for(int c = 0; c * c <= n; c++)
for(int d = c; d * d + c * c <= n; d++)
{
int s = c * c + d * d;
if(h[s] == -1)
h[s] = c, m[s] = d;
}
for(int a = 0; a * a <= n; a++)
for(int b = a; b * b + a * a <= n; b++)
{
int s = n - a * a - b * b;
if(h[s] != -1)
{
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",a , b, h[s], m[s]);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
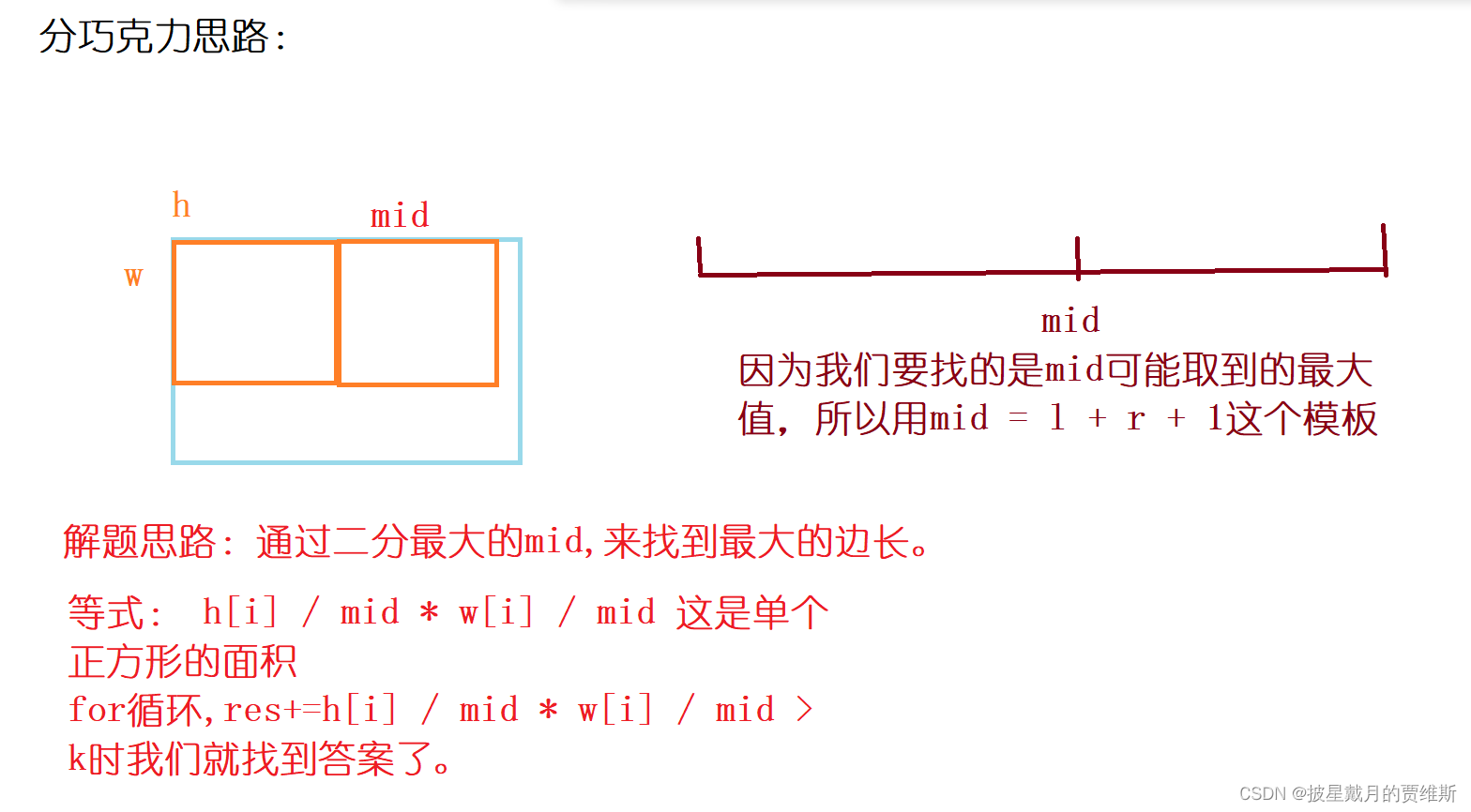
🍇、(AcWing)分巧克力
本题链接: 分巧克力

解题思路:
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100010;
int n, k;
int h[N], w[N];//横竖边长
bool cheak(int mid)
{
LL res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
res += (LL)h[i]/mid *(w[i] / mid);
if(res >= k) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main ()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> h[i] >> w[i];
int l = 1, r = 1e5;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if(cheak(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << r << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
🍇、(AcWing)我在哪?
本题链接: 我在哪?

简单分析题意:本道题的题意还是比较难理解的,题目又长,核心就是这一句:例如,假设沿路的邮箱序列为 ABCDABC 。
约翰不能令 K=3,因为如果他看到了 ABC,则沿路有两个这一连续颜色序列可能所在的位置。
最小可行的 K 的值为 K=4,因为如果他查看任意连续 4 个邮箱,那么可得到的连续颜色序列可以唯一确定他在道路上的位置。
本意等价于:在一个连续的字符串中找到最短的能判断是在这串字符串中唯一出现,这个字符串的长度就是k值。
解题思路:因为这道题的数据量只有100,所以可以直接暴力,也可以二分最小的mid值,两种做法。
暴力代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int n;
string str;
int main ()
{
cin >> n >> str;
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
bool flag = false; //判断两个串是不是相同
for(int i = 0; i + k - 1 <= n; i++)//i + k - 1是这个串的长度
{
for(int j = i + 1; j + k -1 <= n; j++)//j的枚举要从i + 1开始
{
bool Same = true;//判断两个串是不是相同
for(int u = 0; u < k; u++)
if(str[i + u] != str[j + u])
{
Same = false;
break;
}
if(Same)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if(!flag)
{
cout << k << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
二分代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int n;
string str;
bool cheak(int mid)
{
unordered_set<string> hash;
for(int i = 0; i + mid -1 <= n; i++)
{
string s = str.substr(i, mid);
if(hash.count(s)) return false; //如果s已经在哈希表中存在过了,返回false
hash.insert(s);//哈希表中再插入s
}
return true;
}
int main ()
{
cin >> n >> str;
int l = 1, r = n;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(cheak(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << r << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
🍎、总结
本文简要介绍了二分的简要概念和应用场景和经典的二分模板和几道二分的经典例题,希望大家读后能有所收获!
