一、前言
对于C或C++程序员来说,面对的bug很大部分是内存操作问题,这其中比较令人头疼的就是内存泄漏了,虽然我们有valgrind 和AScan等内存问题的检测工具,但是valgrind每次输出一大堆,AScan有时候看输出结果看的是云里雾里的。再说,谁会嫌弃工具箱里面多个工具那。
二、 内存泄漏的一般检查
2.1 基本准备
内存泄漏问题的检查步骤,对于做过c或c++同学都比较熟悉:
首先通过top或vmstat 、或smem(本次介绍)等工具查看内存情况,看看是否出现了内存泄漏。
其次用pidstat 或top指定进程的方式,观察可以进程内存占用情况。
用memleak或gdb工具查看内存泄漏。
先上测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#define MALLOC_SIZE 256000int *fibo(int *n0, int *n1){ int *v = (int *) malloc(MALLOC_SIZE*sizeof(int)); memset(v, 0, MALLOC_SIZE*sizeof(int)); *v = *n0 + *n1; return v;}void do_test(){ int n0 = 0; int n1 = 1; int *v = NULL; int n = 2; for (n = 2; n > 0; n++) { v = fibo(&n0, &n1); n0 = n1; n1 = *v; printf("%dth => %lld\n", n, *v); //free(v) sleep(1); }}int main(void){ printf("pid=%d\n", getpid()); do_test(); return 0;}- 1.
程序比较简单,编译运行起来:
gcc memtest.c ; ./a.out- 1.
2.2 smem工具
这次用下新工具smem,这是一个python写的小工具,可以统计系统中所有进程占用的物理内存RSS、以及去掉共享内存的PSS、以及程序本身的独占内存USS的情况。
安装:
# centos 下yum install epel-releaseyum install smem python-matplotlib python-tk# ubuntu 下apt-get install smem- 1.
常用命令:
-k 带单位显示内存
root@ubuntu-lab:/home/miao# smem -k PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS 1009 root /usr/sbin/cron -f -P 0 304.0K 399.0K 2.9M 1137 root nginx: master process /usr/ 0 196.0K 435.0K 2.1M 931 root /usr/sbin/irqbalance --fore 0 492.0K 655.0K 4.0M ....- 1.
-u -k 带单位显示每个用户的内存占用:
root@ubuntu-lab:/home/miao# smem -u -kUser Count Swap USS PSS RSS systemd-timesync 1 0 764.0K 1.1M 6.7M messagebus 1 0 924.0K 1.2M 4.9M systemd-network 1 0 1.7M 2.1M 7.4M syslog 1 0 3.0M 3.1M 6.2M www-data 4 0 2.0M 4.2M 22.4M systemd-resolve 1 0 4.8M 5.8M 12.7M miao 8 0 11.0M 16.9M 49.1M postgres 7 0 9.2M 22.0M 74.5M mysql 1 0 74.0M 74.7M 80.7M root 30 0 260.7M 284.1M 429.5M- 1.
-w -k 显示系统整体内存情况类似free
root@ubuntu-lab:/home/miao# smem -w -kArea Used Cache Noncache firmware/hardware 0 0 0 kernel image 0 0 0 kernel dynamic memory 1.5G 1.3G 268.5M userspace memory 414.0M 191.5M 222.5M free memory 2.8G 2.8G 0- 1.
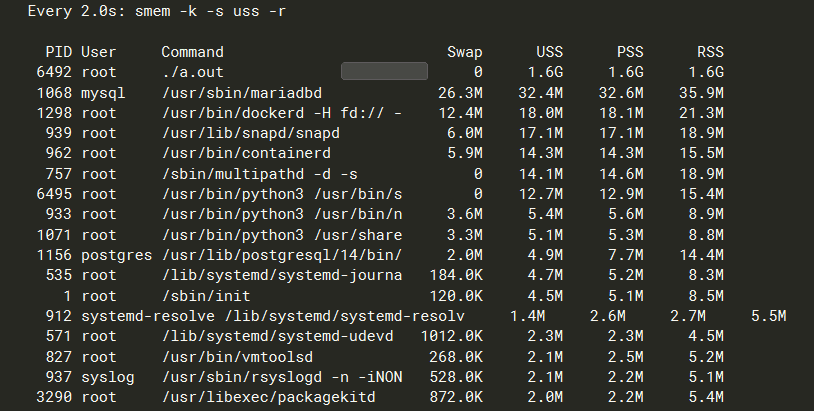
-k -s uss -r 按照uss的占用从大到小排序的方式展示内存的占用情况 非常实用
root@ubuntu-lab:/home/miao# smem -k -s uss -r PID User Command Swap USS PSS RSS 1298 root /usr/bin/dockerd -H 0 74.3M 74.5M 77.9M 1068 mysql /usr/sbin/mariadbd 0 74.0M 74.8M 80.7M 939 root /usr/lib/snapd/snapd 0 44.9M 45.0M 46.7M ....- 1.
好了基本命令介绍完毕,那我们来看看如何查看内存是否泄漏吧,因为内存泄漏的程序占用的内存是一直再增加的(这不是废话嘛),这样我们就可以用上面的排序命令只观察上面几个进程了。
watch smem -k -s uss -r- 1.
小技巧,watch加在命令前面,5s执行一次命令,会高亮显示改变的部分。
2.3 memleak检查
在ubuntu下安装memleak竟然很难安装,我用的是最新的服务器版本,后面在centos下安装后测试的:
[root@xxx]# python2 /usr/share/bcc/tools/memleak -p 160399Attaching to pid 160399, Ctrl+C to quit.[17:27:25] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations: 5120000 bytes in 5 allocations from stack fibo+0x1a [a.out] do_test+0x41 [a.out] main+0x24 [a.out] __libc_start_main+0xf5 [libc-2.17.so][17:27:30] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations: 10240000 bytes in 10 allocations from stack fibo+0x1a [a.out] do_test+0x41 [a.out] main+0x24 [a.out] __libc_start_main+0xf5 [libc-2.17.so][17:27:35] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations: 15360000 bytes in 15 allocations from stack fibo+0x1a [a.out] do_test+0x41 [a.out] main+0x24 [a.out] __libc_start_main+0xf5 [libc-2.17.so][17:27:40] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations: 19456000 bytes in 19 allocations from stack- 1.
fibo 函数出现内存泄漏,把泄漏的字节数都打印了出来,我们改了下代码把free的注释去掉,再用memleak查看等了一会还是没有泄漏信息,说明已经修复了,如下:
[root@xxx]# python2 /usr/share/bcc/tools/memleak -p 165349Attaching to pid 165349, Ctrl+C to quit.[17:35:21] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations:[17:35:26] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations:[17:35:31] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations:[17:35:36] Top 10 stacks with outstanding allocations:- 1.
三、gdb 查看内存泄漏
也许你对memleak已经很熟悉了,那来看看gdb查看函数的内存泄漏方法吧,这个方法只是查看具体的一个函数是否存在内存泄漏,一定的场景下还是蛮实用的。 把代码中的 for (n = 2; n > 0; n++) 改成 for (n = 2; n > 0&& n <10; n++)
(gdb) b mainBreakpoint 1 at 0x400739: file memleaktest.c, line 34.(gdb) rStarting program: /home/miaohq/testcode/./a.out Breakpoint 1, main () at memleaktest.c:3434 printf("pid=%d\n", getpid());Missing separate debuginfos, use: debuginfo-install glibc-2.17-325.el7_9.x86_64(gdb) call malloc_stats()Arena 0:system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0Total (incl. mmap):system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0max mmap regions = 0max mmap bytes = 0$1 = -136490560(gdb) npid=18197735 do_test();(gdb) call malloc_stats()Arena 0:system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0Total (incl. mmap):system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0max mmap regions = 0max mmap bytes = 0$2 = -136490560(gdb) n2th => 13th => 24th => 35th => 56th => 87th => 138th => 219th => 3436 return 0;(gdb) call malloc_stats()Arena 0:system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0Total (incl. mmap):system bytes = 8224768in use bytes = 8224768max mmap regions = 8max mmap bytes = 8224768$3 = -136490560(gdb) p 256000*4*8$4 = 8192000(gdb)- 1.
Total (incl. mmap):即本程序占用的总内存,看到明显的增加部分即为未释放的内存,程序使用的内存增加:8224768 稍大于 256000*4*8 分配的内存,内存分配需要存储链表还有一些对齐原因所以会多分配些。
free之后的场景:
(gdb) call malloc_stats()Arena 0:system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0Total (incl. mmap):system bytes = 0in use bytes = 0max mmap regions = 0max mmap bytes = 0$1 = -136490560(gdb) npid=18340635 do_test();(gdb) n2th => 13th => 24th => 35th => 56th => 87th => 138th => 219th => 3436 return 0;(gdb) call malloc_stats()Arena 0:system bytes = 1159168in use bytes = 0Total (incl. mmap):system bytes = 1159168in use bytes = 0max mmap regions = 1max mmap bytes = 1028096$2 = -136490560(gdb)- 1.
in use bytes 为0了。