Diffusion扩散模型学习1——Pytorch搭建DDPM利用深度卷积神经网络实现图片生成
- 学习前言
- 源码下载地址
- 网络构建
- 一、什么是Diffusion
- 1、加噪过程
- 2、去噪过程
- 二、DDPM网络的构建(Unet网络的构建)
- 三、Diffusion的训练思路
- 利用DDPM生成图片
- 一、数据集的准备
- 二、数据集的处理
- 三、模型训练
学习前言
我又死了我又死了我又死了!

源码下载地址
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/ddpm-pytorch
喜欢的可以点个star噢。
网络构建
一、什么是Diffusion
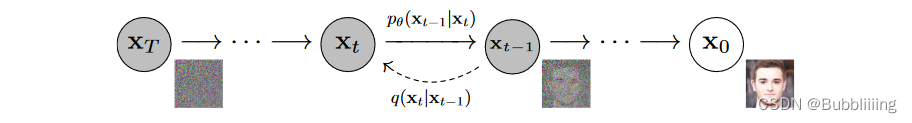
如上图所示。DDPM模型主要分为两个过程:
1、Forward加噪过程(从右往左),数据集的真实图片中逐步加入高斯噪声,最终变成一个杂乱无章的高斯噪声,这个过程一般发生在训练的时候。加噪过程满足一定的数学规律。
2、Reverse去噪过程(从左往右),指对加了噪声的图片逐步去噪,从而还原出真实图片,这个过程一般发生在预测生成的时候。尽管在这里说的是加了噪声的图片,但实际去预测生成的时候,是随机生成一个高斯噪声来去噪。去噪的时候不断根据
X
t
X_t
Xt的图片生成
X
t
−
1
X_{t-1}
Xt−1的噪声,从而实现图片的还原。
1、加噪过程
Forward加噪过程主要符合如下的公式:
x
t
=
α
t
x
t
−
1
+
1
−
α
t
z
1
x_t=\sqrt{\alpha_t} x_{t-1}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t} z_{1}
xt=αtxt−1+1−αtz1
其中
α
t
\sqrt{\alpha_t}
αt是预先设定好的超参数,被称为Noise schedule,通常是小于1的值,在论文中
α
t
\alpha_t
αt的值从0.9999到0.998。
ϵ
t
−
1
∼
N
(
0
,
1
)
\epsilon_{t-1} \sim N(0, 1)
ϵt−1∼N(0,1)是高斯噪声。由公式(1)迭代推导。
x t = a t ( a t − 1 x t − 2 + 1 − α t − 1 z 2 ) + 1 − α t z 1 = a t a t − 1 x t − 2 + ( a t ( 1 − α t − 1 ) z 2 + 1 − α t z 1 ) x_t=\sqrt{a_t}\left(\sqrt{a_{t-1}} x_{t-2}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_{t-1}} z_2\right)+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t} z_1=\sqrt{a_t a_{t-1}} x_{t-2}+\left(\sqrt{a_t\left(1-\alpha_{t-1}\right)} z_2+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t} z_1\right) xt=at(at−1xt−2+1−αt−1z2)+1−αtz1=atat−1xt−2+(at(1−αt−1)z2+1−αtz1)
其中每次加入的噪声都服从高斯分布
z
1
,
z
2
,
…
∼
N
(
0
,
1
)
z_1, z_2, \ldots \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)
z1,z2,…∼N(0,1),两个高斯分布的相加高斯分布满足公式:
N
(
0
,
σ
1
2
)
+
N
(
0
,
σ
2
2
)
∼
N
(
0
,
(
σ
1
2
+
σ
2
2
)
)
\mathcal{N}\left(0, \sigma_1^2 \right)+\mathcal{N}\left(0, \sigma_2^2 \right) \sim \mathcal{N}\left(0,\left(\sigma_1^2+\sigma_2^2\right) \right)
N(0,σ12)+N(0,σ22)∼N(0,(σ12+σ22)),因此,得到
x
t
x_t
xt的公式为:
x
t
=
a
t
a
t
−
1
x
t
−
2
+
1
−
α
t
α
t
−
1
z
2
x_t = \sqrt{a_t a_{t-1}} x_{t-2}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t \alpha_{t-1}} z_2
xt=atat−1xt−2+1−αtαt−1z2
因此不断往里面套,就能发现规律了,其实就是累乘
可以直接得出
x
0
x_0
x0到
x
t
x_t
xt的公式:
x
t
=
α
t
‾
x
0
+
1
−
α
t
‾
z
t
x_t=\sqrt{\overline{\alpha_t}} x_0+\sqrt{1-\overline{\alpha_t}} z_t
xt=αtx0+1−αtzt
其中 α t ‾ = ∏ i t α i \overline{\alpha_t}=\prod_i^t \alpha_i αt=∏itαi,这是随Noise schedule设定好的超参数, z t − 1 ∼ N ( 0 , 1 ) z_{t-1} \sim N(0, 1) zt−1∼N(0,1)也是一个高斯噪声。通过上述两个公式,我们可以不断的将图片进行破坏加噪。
2、去噪过程
反向过程就是通过估测噪声,多次迭代逐渐将被破坏的
x
t
x_t
xt恢复成
x
0
x_0
x0,在恢复时刻,我们已经知道的是
x
t
x_t
xt,这是图片在
t
t
t时刻的噪声图。一下子从
x
t
x_t
xt恢复成
x
0
x_0
x0是不可能的,我们只能一步一步的往前推,首先从
x
t
x_t
xt恢复成
x
t
−
1
x_{t-1}
xt−1。根据贝叶斯公式,已知
x
t
x_t
xt反推
x
t
−
1
x_{t-1}
xt−1:
q
(
x
t
−
1
∣
x
t
,
x
0
)
=
q
(
x
t
∣
x
t
−
1
,
x
0
)
q
(
x
t
−
1
∣
x
0
)
q
(
x
t
∣
x
0
)
q\left(x_{t-1} \mid x_t, x_0\right)=q\left(x_t \mid x_{t-1}, x_0\right) \frac{q\left(x_{t-1} \mid x_0\right)}{q\left(x_t \mid x_0\right)}
q(xt−1∣xt,x0)=q(xt∣xt−1,x0)q(xt∣x0)q(xt−1∣x0)
右边的三个东西都可以从x_0开始推得到:
q
(
x
t
−
1
∣
x
0
)
=
a
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
+
1
−
a
ˉ
t
−
1
z
∼
N
(
a
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
,
1
−
a
ˉ
t
−
1
)
q\left(x_{t-1} \mid x_0\right)=\sqrt{\bar{a}_{t-1}} x_0+\sqrt{1-\bar{a}_{t-1}} z \sim \mathcal{N}\left(\sqrt{\bar{a}_{t-1}} x_0, 1-\bar{a}_{t-1}\right)
q(xt−1∣x0)=aˉt−1x0+1−aˉt−1z∼N(aˉt−1x0,1−aˉt−1)
q
(
x
t
∣
x
0
)
=
a
ˉ
t
x
0
+
1
−
α
ˉ
t
z
∼
N
(
a
ˉ
t
x
0
,
1
−
α
ˉ
t
)
q\left(x_t \mid x_0\right) = \sqrt{\bar{a}_t} x_0+\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_t} z \sim \mathcal{N}\left(\sqrt{\bar{a}_t} x_0 , 1-\bar{\alpha}_t\right)
q(xt∣x0)=aˉtx0+1−αˉtz∼N(aˉtx0,1−αˉt)
q
(
x
t
∣
x
t
−
1
,
x
0
)
=
a
t
x
t
−
1
+
1
−
α
t
z
∼
N
(
a
t
x
t
−
1
,
1
−
α
t
)
q\left(x_t \mid x_{t-1}, x_0\right)=\sqrt{a_t} x_{t-1}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t} z \sim \mathcal{N}\left(\sqrt{a_t} x_{t-1}, 1-\alpha_t\right) \\
q(xt∣xt−1,x0)=atxt−1+1−αtz∼N(atxt−1,1−αt)
因此,由于右边三个东西均满足正态分布,
q
(
x
t
−
1
∣
x
t
,
x
0
)
q\left(x_{t-1} \mid x_t, x_0\right)
q(xt−1∣xt,x0)满足分布如下:
∝
exp
(
−
1
2
(
(
x
t
−
α
t
x
t
−
1
)
2
β
t
+
(
x
t
−
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
)
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
−
(
x
t
−
α
ˉ
t
x
0
)
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
)
)
\propto \exp \left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{\left(x_t-\sqrt{\alpha_t} x_{t-1}\right)^2}{\beta_t}+\frac{\left(x_{t-1}-\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}} x_0\right)^2}{1-\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}}-\frac{\left(x_t-\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t} x_0\right)^2}{1-\bar{\alpha}_t}\right)\right)
∝exp(−21(βt(xt−αtxt−1)2+1−αˉt−1(xt−1−αˉt−1x0)2−1−αˉt(xt−αˉtx0)2))
把标准正态分布展开后,乘法就相当于加,除法就相当于减,把他们汇总
接下来继续化简,咱们现在要求的是上一时刻的分布
∝
exp
(
−
1
2
(
(
x
t
−
α
t
x
t
−
1
)
2
β
t
+
(
x
t
−
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
)
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
−
(
x
t
−
α
ˉ
t
x
0
)
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
)
)
=
exp
(
−
1
2
(
x
t
2
−
2
α
t
x
t
x
t
−
1
+
α
t
x
t
−
1
2
β
t
+
x
t
−
1
2
−
2
α
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
x
t
−
1
+
α
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
−
(
x
t
−
α
ˉ
t
x
0
)
2
1
−
α
ˉ
t
)
)
=
exp
(
−
1
2
(
(
α
t
β
t
+
1
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
)
x
t
−
1
2
−
(
2
α
t
β
t
x
t
+
2
α
ˉ
t
−
1
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
x
0
)
x
t
−
1
+
C
(
x
t
,
x
0
)
)
)
∝exp(−12((xt−√αtxt−1)2βt+(xt−1−√ˉαt−1x0)21−ˉαt−1−(xt−√ˉαtx0)21−ˉαt))=exp(−12(x2t−2√αtxtxt−1+αtx2t−1βt+x2t−1−2√ˉαt−1x0xt−1+ˉαt−1x201−ˉαt−1−(xt−√ˉαtx0)21−ˉαt))=exp(−12((αtβt+11−ˉαt−1)x2t−1−(2√αtβtxt+2√ˉαt−11−ˉαt−1x0)xt−1+C(xt,x0)))
∝exp(−21(βt(xt−αtxt−1)2+1−αˉt−1(xt−1−αˉt−1x0)2−1−αˉt(xt−αˉtx0)2))=exp(−21(βtxt2−2αtxtxt−1+αtxt−12+1−αˉt−1xt−12−2αˉt−1x0xt−1+αˉt−1x02−1−αˉt(xt−αˉtx0)2))=exp(−21((βtαt+1−αˉt−11)xt−12−(βt2αtxt+1−αˉt−12αˉt−1x0)xt−1+C(xt,x0)))
正态分布满足公式,
exp
(
−
(
x
−
μ
)
2
2
σ
2
)
=
exp
(
−
1
2
(
1
σ
2
x
2
−
2
μ
σ
2
x
+
μ
2
σ
2
)
)
\exp \left(-\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2 \sigma^2}\right)=\exp \left(-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{\sigma^2} x^2-\frac{2 \mu}{\sigma^2} x+\frac{\mu^2}{\sigma^2}\right)\right)
exp(−2σ2(x−μ)2)=exp(−21(σ21x2−σ22μx+σ2μ2)),其中
σ
\sigma
σ就是方差,
μ
\mu
μ就是均值,配方后我们就可以获得均值和方差。
此时的均值为:
μ
~
t
(
x
t
,
x
0
)
=
α
t
(
1
−
α
ˉ
t
−
1
)
1
−
α
ˉ
t
x
t
+
α
ˉ
t
−
1
β
t
1
−
α
ˉ
t
x
0
\tilde{\mu}_t\left(x_t, x_0\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\alpha_t}\left(1-\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}\right)}{1-\bar{\alpha}_t} x_t+\frac{\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}} \beta_t}{1-\bar{\alpha}_t} x_0
μ~t(xt,x0)=1−αˉtαt(1−αˉt−1)xt+1−αˉtαˉt−1βtx0。根据之前的公式,
x
t
=
α
t
‾
x
0
+
1
−
α
t
‾
z
t
x_t=\sqrt{\overline{\alpha_t}} x_0+\sqrt{1-\overline{\alpha_t}} z_t
xt=αtx0+1−αtzt,我们可以使用
x
t
x_t
xt反向估计
x
0
x_0
x0得到
x
0
x_0
x0满足分布
x
0
=
1
α
ˉ
t
(
x
t
−
1
−
α
ˉ
t
z
t
)
x_0=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\bar{\alpha}_t}}\left(\mathrm{x}_t-\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_t} z_t\right)
x0=αˉt1(xt−1−αˉtzt)。最终得到均值为
μ
~
t
=
1
a
t
(
x
t
−
β
t
1
−
a
ˉ
t
z
t
)
\tilde{\mu}_t=\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_t}}\left(x_t-\frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1-\bar{a}_t}} z_t\right)
μ~t=at1(xt−1−aˉtβtzt) ,
z
t
z_t
zt代表t时刻的噪音是什么。由
z
t
z_t
zt无法直接获得,网络便通过当前时刻的
x
t
x_t
xt经过神经网络计算
z
t
z_t
zt。
ϵ
θ
(
x
t
,
t
)
\epsilon_\theta\left(x_t, t\right)
ϵθ(xt,t)也就是上面提到的
z
t
z_t
zt。
ϵ
θ
\epsilon_\theta
ϵθ代表神经网络。
x
t
−
1
=
1
α
t
(
x
t
−
1
−
α
t
1
−
α
ˉ
t
ϵ
θ
(
x
t
,
t
)
)
+
σ
t
z
x_{t-1}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}}\left(x_t-\frac{1-\alpha_t}{\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon_\theta\left(x_t, t\right)\right)+\sigma_t z
xt−1=αt1(xt−1−αˉt1−αtϵθ(xt,t))+σtz
由于加噪过程中的真实噪声
ϵ
\epsilon
ϵ在复原过程中是无法获得的,因此DDPM的关键就是训练一个由
x
t
x_t
xt和
t
t
t估测橾声的模型
ϵ
θ
(
x
t
,
t
)
\epsilon_\theta\left(x_t, t\right)
ϵθ(xt,t),其中
θ
\theta
θ就是模型的训练参数,
σ
t
\sigma_t
σt 也是一个高斯噪声
σ
t
∼
N
(
0
,
1
)
\sigma_t \sim N(0,1)
σt∼N(0,1),用于表示估测与实际的差距。在DDPM中,使用U-Net作为估测噪声的模型。
本质上,我们就是训练这个Unet模型,该模型输入为 x t x_t xt和 t t t,输出为 x t x_t xt时刻的高斯噪声。即利用 x t x_t xt和 t t t预测这一时刻的高斯噪声。这样就可以一步一步的再从噪声回到真实图像。
二、DDPM网络的构建(Unet网络的构建)
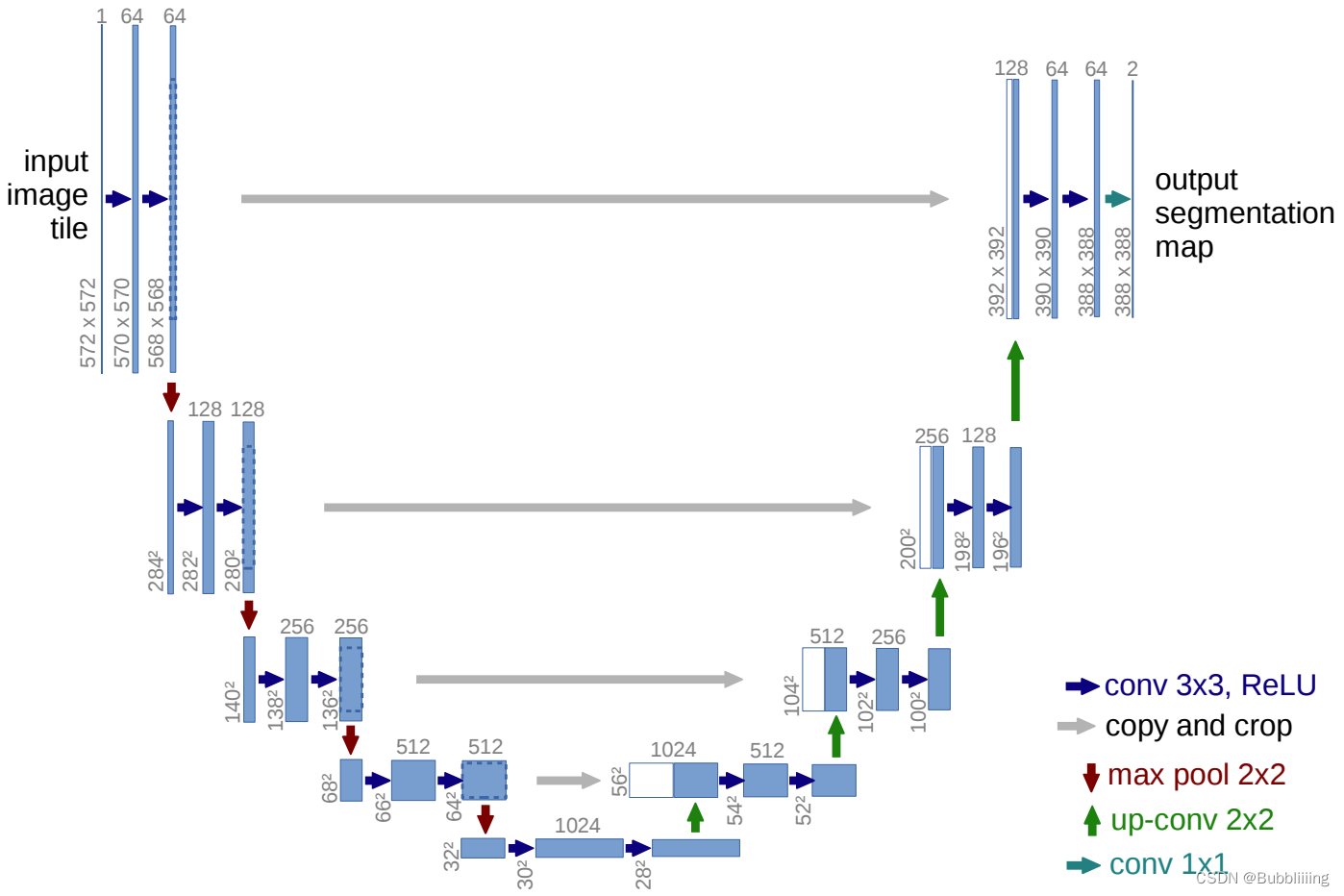
上图是典型的Unet模型结构,仅仅作为示意图,里面具体的数字同学们无需在意,和本文的学习无关。在本文中,Unet的输入和输出shape相同,通道均为3(一般为RGB三通道),宽高相同。
本质上,DDPM最重要的工作就是训练Unet模型,该模型输入为 x t x_t xt和 t t t,输出为 x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1时刻的高斯噪声。即利用 x t x_t xt和 t t t预测上一时刻的高斯噪声。这样就可以一步一步的再从噪声回到真实图像。
假设我们需要生成一个[64, 64, 3]的图像,在 t t t时刻,我们有一个 x t x_t xt噪声图,该噪声图的的shape也为[64, 64, 3],我们将它和 t t t一起输入到Unet中。Unet的输出为 x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1时刻的[64, 64, 3]的噪声。
实现代码如下,代码中的特征提取模块为残差结构,方便优化:
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def get_norm(norm, num_channels, num_groups):
if norm == "in":
return nn.InstanceNorm2d(num_channels, affine=True)
elif norm == "bn":
return nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
elif norm == "gn":
return nn.GroupNorm(num_groups, num_channels)
elif norm is None:
return nn.Identity()
else:
raise ValueError("unknown normalization type")
#------------------------------------------#
# 计算时间步长的位置嵌入。
# 一半为sin,一半为cos。
#------------------------------------------#
class PositionalEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, scale=1.0):
super().__init__()
assert dim % 2 == 0
self.dim = dim
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, x):
device = x.device
half_dim = self.dim // 2
emb = math.log(10000) / half_dim
emb = torch.exp(torch.arange(half_dim, device=device) * -emb)
# x * self.scale和emb外积
emb = torch.outer(x * self.scale, emb)
emb = torch.cat((emb.sin(), emb.cos()), dim=-1)
return emb
#------------------------------------------#
# 下采样层,一个步长为2x2的卷积
#------------------------------------------#
class Downsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super().__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
def forward(self, x, time_emb, y):
if x.shape[2] % 2 == 1:
raise ValueError("downsampling tensor height should be even")
if x.shape[3] % 2 == 1:
raise ValueError("downsampling tensor width should be even")
return self.downsample(x)
#------------------------------------------#
# 上采样层,Upsample+卷积
#------------------------------------------#
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super().__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest"),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, padding=1),
)
def forward(self, x, time_emb, y):
return self.upsample(x)
#------------------------------------------#
# 使用Self-Attention注意力机制
# 做一个全局的Self-Attention
#------------------------------------------#
class AttentionBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, norm="gn", num_groups=32):
super().__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.norm = get_norm(norm, in_channels, num_groups)
self.to_qkv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels * 3, 1)
self.to_out = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 1)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
q, k, v = torch.split(self.to_qkv(self.norm(x)), self.in_channels, dim=1)
q = q.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(b, h * w, c)
k = k.view(b, c, h * w)
v = v.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(b, h * w, c)
dot_products = torch.bmm(q, k) * (c ** (-0.5))
assert dot_products.shape == (b, h * w, h * w)
attention = torch.softmax(dot_products, dim=-1)
out = torch.bmm(attention, v)
assert out.shape == (b, h * w, c)
out = out.view(b, h, w, c).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return self.to_out(out) + x
#------------------------------------------#
# 用于特征提取的残差结构
#------------------------------------------#
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, in_channels, out_channels, dropout, time_emb_dim=None, num_classes=None, activation=F.relu,
norm="gn", num_groups=32, use_attention=False,
):
super().__init__()
self.activation = activation
self.norm_1 = get_norm(norm, in_channels, num_groups)
self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1)
self.norm_2 = get_norm(norm, out_channels, num_groups)
self.conv_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=dropout),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1),
)
self.time_bias = nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, out_channels) if time_emb_dim is not None else None
self.class_bias = nn.Embedding(num_classes, out_channels) if num_classes is not None else None
self.residual_connection = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1) if in_channels != out_channels else nn.Identity()
self.attention = nn.Identity() if not use_attention else AttentionBlock(out_channels, norm, num_groups)
def forward(self, x, time_emb=None, y=None):
out = self.activation(self.norm_1(x))
# 第一个卷积
out = self.conv_1(out)
# 对时间time_emb做一个全连接,施加在通道上
if self.time_bias is not None:
if time_emb is None:
raise ValueError("time conditioning was specified but time_emb is not passed")
out += self.time_bias(self.activation(time_emb))[:, :, None, None]
# 对种类y_emb做一个全连接,施加在通道上
if self.class_bias is not None:
if y is None:
raise ValueError("class conditioning was specified but y is not passed")
out += self.class_bias(y)[:, :, None, None]
out = self.activation(self.norm_2(out))
# 第二个卷积+残差边
out = self.conv_2(out) + self.residual_connection(x)
# 最后做个Attention
out = self.attention(out)
return out
#------------------------------------------#
# Unet模型
#------------------------------------------#
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, img_channels, base_channels=128, channel_mults=(1, 2, 2, 2),
num_res_blocks=2, time_emb_dim=128 * 4, time_emb_scale=1.0, num_classes=None, activation=F.silu,
dropout=0.1, attention_resolutions=(1,), norm="gn", num_groups=32, initial_pad=0,
):
super().__init__()
# 使用到的激活函数,一般为SILU
self.activation = activation
# 是否对输入进行padding
self.initial_pad = initial_pad
# 需要去区分的类别数
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 对时间轴输入的全连接层
self.time_mlp = nn.Sequential(
PositionalEmbedding(base_channels, time_emb_scale),
nn.Linear(base_channels, time_emb_dim),
nn.SiLU(),
nn.Linear(time_emb_dim, time_emb_dim),
) if time_emb_dim is not None else None
# 对输入图片的第一个卷积
self.init_conv = nn.Conv2d(img_channels, base_channels, 3, padding=1)
# self.downs用于存储下采样用到的层,首先利用ResidualBlock提取特征
# 然后利用Downsample降低特征图的高宽
self.downs = nn.ModuleList()
self.ups = nn.ModuleList()
# channels指的是每一个模块处理后的通道数
# now_channels是一个中间变量,代表中间的通道数
channels = [base_channels]
now_channels = base_channels
for i, mult in enumerate(channel_mults):
out_channels = base_channels * mult
for _ in range(num_res_blocks):
self.downs.append(
ResidualBlock(
now_channels, out_channels, dropout,
time_emb_dim=time_emb_dim, num_classes=num_classes, activation=activation,
norm=norm, num_groups=num_groups, use_attention=i in attention_resolutions,
)
)
now_channels = out_channels
channels.append(now_channels)
if i != len(channel_mults) - 1:
self.downs.append(Downsample(now_channels))
channels.append(now_channels)
# 可以看作是特征整合,中间的一个特征提取模块
self.mid = nn.ModuleList(
[
ResidualBlock(
now_channels, now_channels, dropout,
time_emb_dim=time_emb_dim, num_classes=num_classes, activation=activation,
norm=norm, num_groups=num_groups, use_attention=True,
),
ResidualBlock(
now_channels, now_channels, dropout,
time_emb_dim=time_emb_dim, num_classes=num_classes, activation=activation,
norm=norm, num_groups=num_groups, use_attention=False,
),
]
)
# 进行上采样,进行特征融合
for i, mult in reversed(list(enumerate(channel_mults))):
out_channels = base_channels * mult
for _ in range(num_res_blocks + 1):
self.ups.append(ResidualBlock(
channels.pop() + now_channels, out_channels, dropout,
time_emb_dim=time_emb_dim, num_classes=num_classes, activation=activation,
norm=norm, num_groups=num_groups, use_attention=i in attention_resolutions,
))
now_channels = out_channels
if i != 0:
self.ups.append(Upsample(now_channels))
assert len(channels) == 0
self.out_norm = get_norm(norm, base_channels, num_groups)
self.out_conv = nn.Conv2d(base_channels, img_channels, 3, padding=1)
def forward(self, x, time=None, y=None):
# 是否对输入进行padding
ip = self.initial_pad
if ip != 0:
x = F.pad(x, (ip,) * 4)
# 对时间轴输入的全连接层
if self.time_mlp is not None:
if time is None:
raise ValueError("time conditioning was specified but tim is not passed")
time_emb = self.time_mlp(time)
else:
time_emb = None
if self.num_classes is not None and y is None:
raise ValueError("class conditioning was specified but y is not passed")
# 对输入图片的第一个卷积
x = self.init_conv(x)
# skips用于存放下采样的中间层
skips = [x]
for layer in self.downs:
x = layer(x, time_emb, y)
skips.append(x)
# 特征整合与提取
for layer in self.mid:
x = layer(x, time_emb, y)
# 上采样并进行特征融合
for layer in self.ups:
if isinstance(layer, ResidualBlock):
x = torch.cat([x, skips.pop()], dim=1)
x = layer(x, time_emb, y)
# 上采样并进行特征融合
x = self.activation(self.out_norm(x))
x = self.out_conv(x)
if self.initial_pad != 0:
return x[:, :, ip:-ip, ip:-ip]
else:
return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
三、Diffusion的训练思路
Diffusion的训练思路比较简单,首先随机给每个batch里每张图片都生成一个t,代表我选择这个batch里面第t个时刻的噪声进行拟合。代码如下:
t = torch.randint(0, self.num_timesteps, (b,), device=device)
- 1
生成batch_size个噪声,计算施加这个噪声后模型在t个时刻的噪声图片是怎么样的,如下所示:
def perturb_x(self, x, t, noise):
return (
extract(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape) * x +
extract(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape) * noise
)
def get_losses(self, x, t, y):
# x, noise [batch_size, 3, 64, 64]
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
perturbed_x = self.perturb_x(x, t, noise)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
之后利用这个噪声图片、t和网络模型计算预测噪声,利用预测噪声和实际噪声进行拟合。
def get_losses(self, x, t, y):
# x, noise [batch_size, 3, 64, 64]
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
perturbed_x = self.perturb_x(x, t, noise)
estimated_noise = self.model(perturbed_x, t, y)
if self.loss_type == "l1":
loss = F.l1_loss(estimated_noise, noise)
elif self.loss_type == "l2":
loss = F.mse_loss(estimated_noise, noise)
return loss
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
利用DDPM生成图片
DDPM的库整体结构如下:
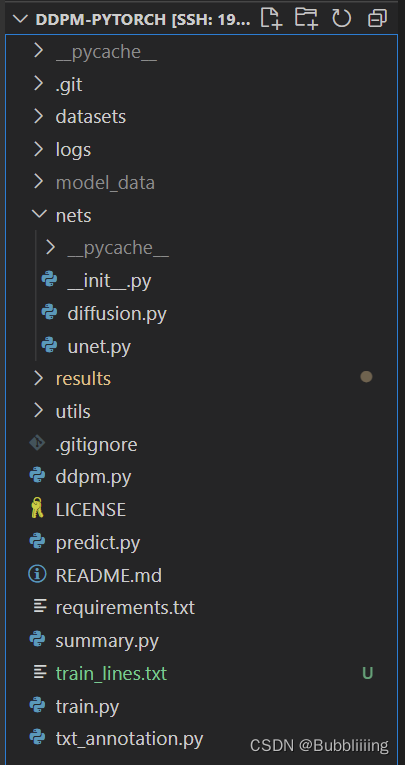
一、数据集的准备
在训练前需要准备好数据集,数据集保存在datasets文件夹里面。
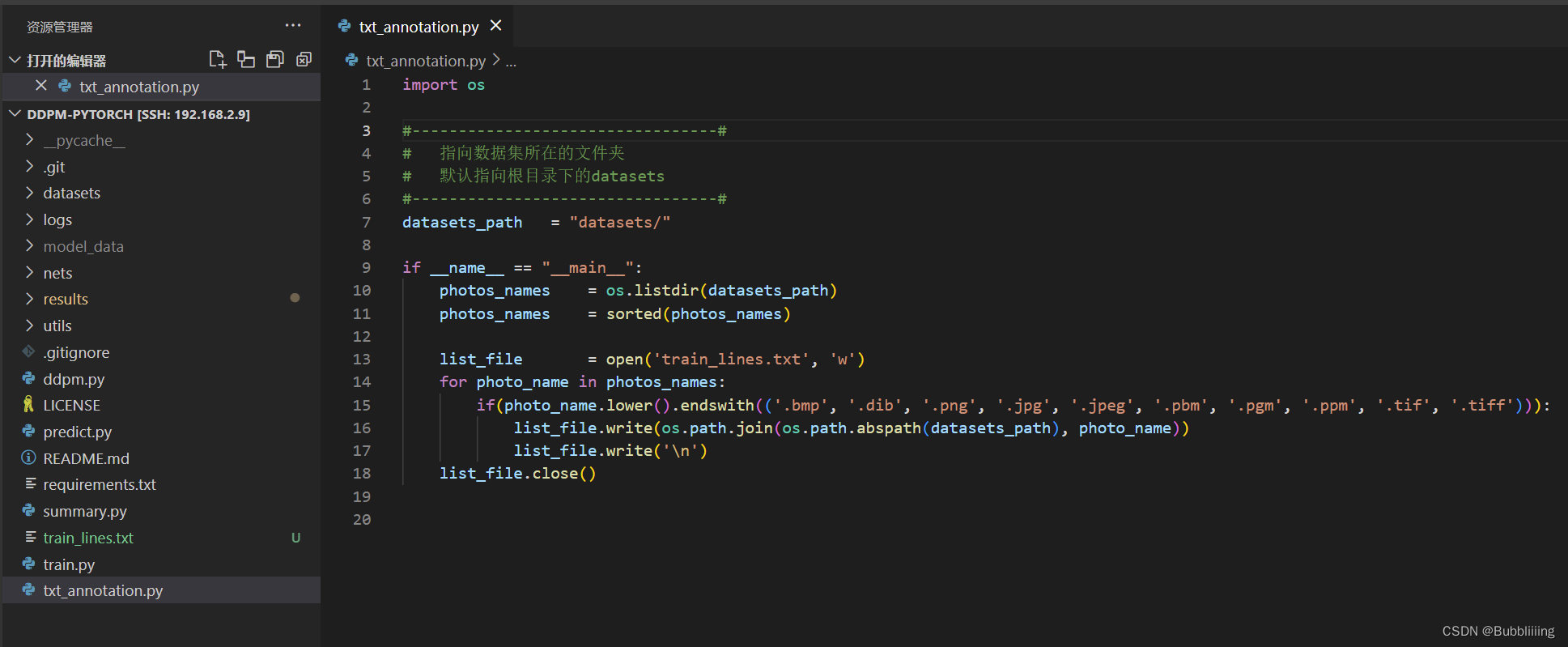
二、数据集的处理
打开txt_annotation.py,默认指向根目录下的datasets。运行txt_annotation.py。
此时生成根目录下面的train_lines.txt。
三、模型训练
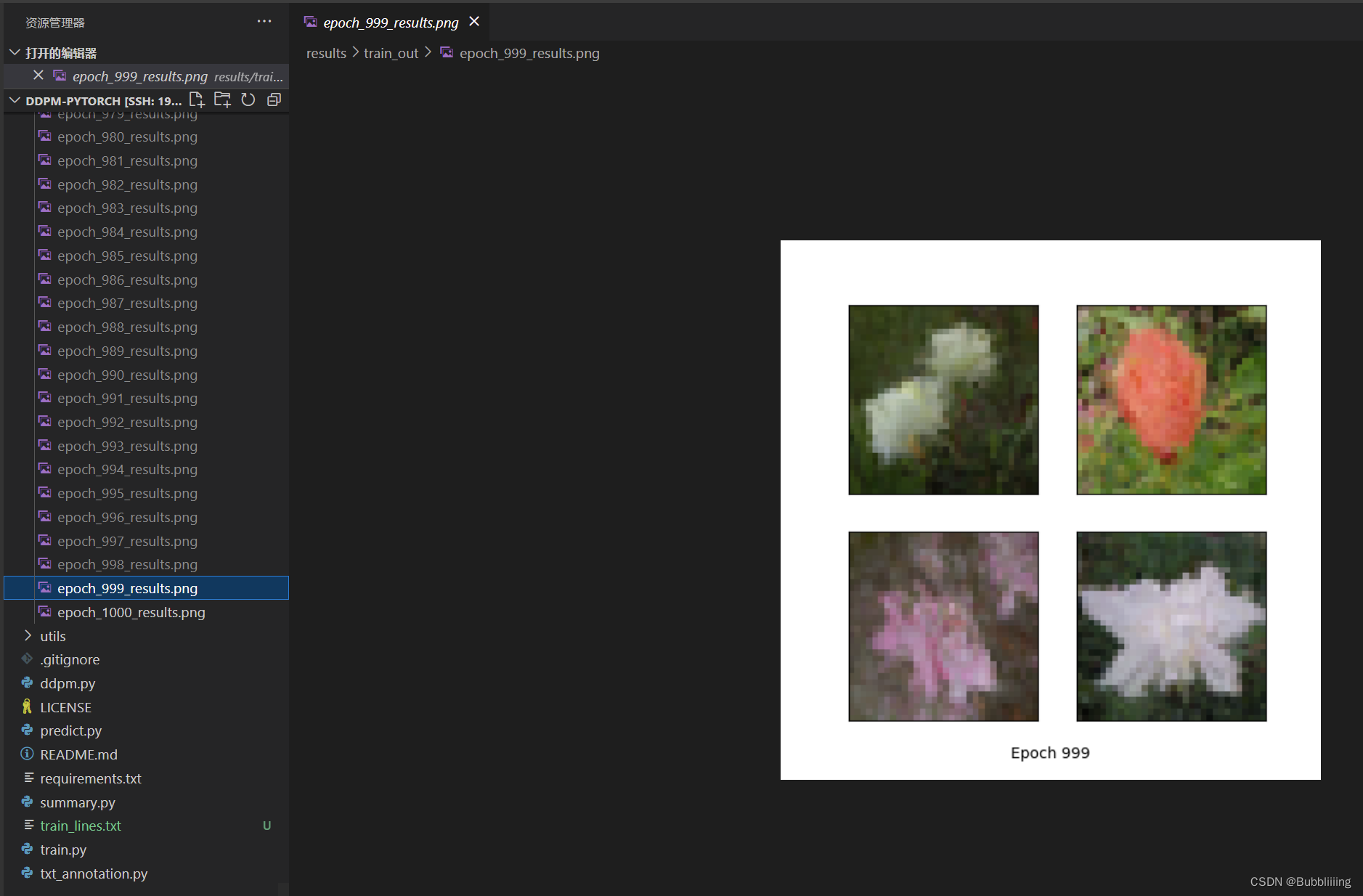
在完成数据集处理后,运行train.py即可开始训练。

训练过程中,可在results文件夹内查看训练效果:

 微信公众号
微信公众号

