各位CSDN的uu们你们好呀,今天小雅兰又来更新新专栏啦,其实之前我就已经写过了顺序表的内容,只是之前的内容不是最新版的顺序表,现在,我来更新一下最新版的顺序表,下面,就让我们进入更新版的顺序表的世界吧
顺序表和小雅兰之前写的三子棋、扫雷、通讯录一样,分为三个文件:
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/128705747?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/128717749?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/128717749?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129788167?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129896970?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
test.c——测试代码功能
SeqList.c——顺序表的实现
SeqList.h——顺序表的声明
https://xiaoyalan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/129380414?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
这是小雅兰之前写的顺序表的知识,有兴趣的可以去看看
我们写的是一个动态版的顺序表:
把struct SeqList这个结构体重命名为SL
typedef int SLDataType;把int重命名为SLDataType
写成这样的形式是因为:如果以后想要修改类型,那就直接改int就可以了,如果不这样写, 要改很多个地方,就很麻烦
顺序表的初始化:
动态开辟出4个SLDataType类型的大小的空间
顺序表的销毁:也就是把空间还给操作系统
打印顺序表的内容:
尾插:
在这里,我们需要想一个问题:在尾插的过程中,如果空间不够了该怎么办呢???所以在这里,我们还需要一个检查容量的函数,如果容量不够就扩容
下面,我们来测试一下尾插的功能,看是否成功
- int main()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushBack(&s, 5);
- SLPushBack(&s, 6);
- SLPushBack(&s, 7);
- SLPushBack(&s, 8);
- SLPushBack(&s, 9);
- SLPushBack(&s, 10);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- return 0;
- }
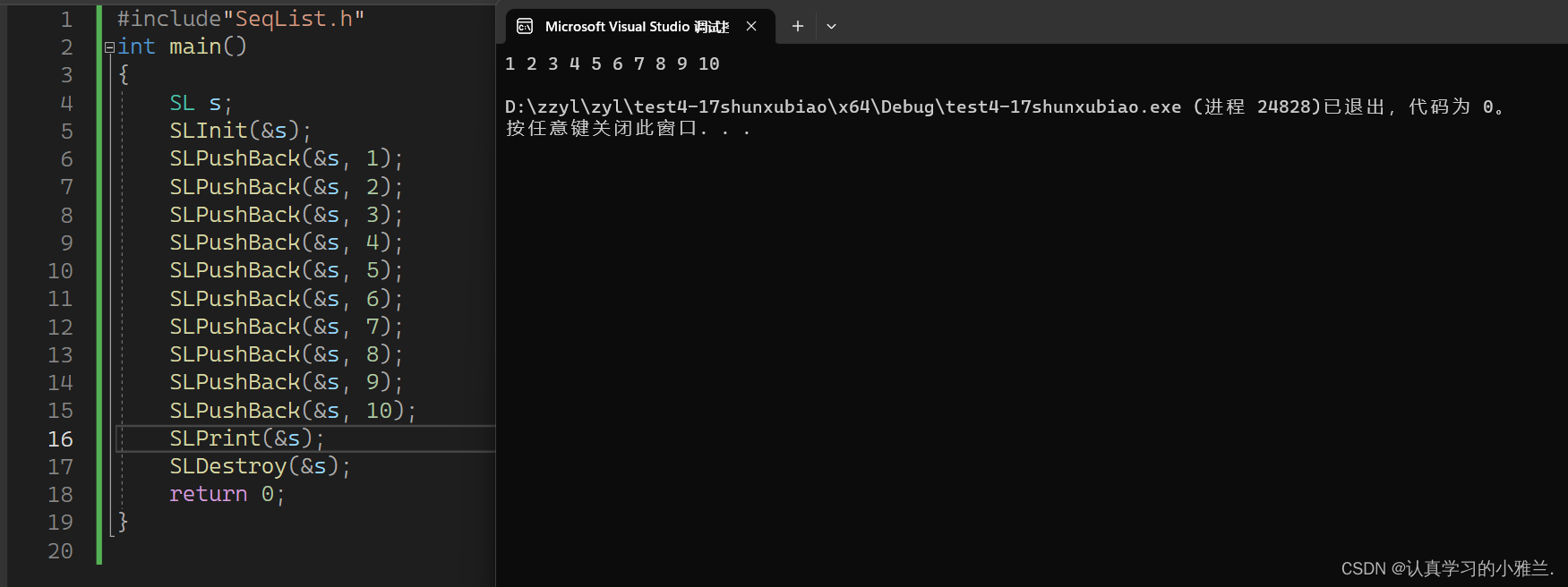
结果发现,尾插的功能非常成功!!!
头插:
需要从后往前挪动数据!!!
若是从前往后挪动数据,就会覆盖,这是绝对不行的
来测试一下头插的功能:
- //头插测试
- void TestSeqList2()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushFront(&s, 5);
- SLPushFront(&s, 6);
- SLPushFront(&s, 7);
- SLPushFront(&s, 8);
- SLPushFront(&s, 9);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- }

尾删:
直接把size--就可以了
来测试一下尾删的功能:
- //尾删测试
- void TestSeqList3()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushFront(&s, 5);
- SLPushFront(&s, 6);
- SLPushFront(&s, 7);
- SLPushFront(&s, 8);
- SLPushFront(&s, 9);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- }

但是这个尾删仍然有点问题,需要检查一下:
头删:
来测试一下头删的功能:
- //头删测试
- void TestSeqList4()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushFront(&s, 5);
- SLPushFront(&s, 6);
- SLPushFront(&s, 7);
- SLPushFront(&s, 8);
- SLPushFront(&s, 9);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- }

在中间位置插入数据:
写了这个函数的功能之后,我们就可以把之前写的头插和尾插修改一下:
但是,这个在中间插入数据的代码还是有点问题;
- //中间插数据测试
- void TestSeqList5()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushFront(&s, 5);
- SLPushFront(&s, 6);
- SLPushFront(&s, 7);
- SLPushFront(&s, 8);
- SLPushFront(&s, 9);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLInsert(&s, 2, 30);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLInsert(&s, 20, 300);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- }

从此运行结果可知:越界是不会报错的!!!但是它的的确确越界了!!!
所以把代码改进为:
- //在中间位置(pos)插入数据
- void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps1->size);
- SLCheckCapacity(ps1);
- int end = ps1->size - 1;
- while (end >= pos)
- {
- ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];
- end--;
- }
- ps1->a[pos] = x;
- ps1->size++;
- }
在中间位置删除数据:
同样,有了这个功能之后,可以把头删和尾删修改一下:
测试一下从中间删除数据的功能:
- //中间删数据测试
- void TestSeqList6()
- {
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- SLPushBack(&s, 1);
- SLPushBack(&s, 2);
- SLPushBack(&s, 3);
- SLPushBack(&s, 4);
- SLPushFront(&s, 5);
- SLPushFront(&s, 6);
- SLPushFront(&s, 7);
- SLPushFront(&s, 8);
- SLPushFront(&s, 9);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPopBack(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPopFront(&s);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLInsert(&s, 2, 30);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLErase(&s, 3);
- SLPrint(&s);
- SLDestroy(&s);
- }

查找:
修改:
下面,浅浅附上一波源代码:
SeqList.c的内容
- #include"SeqList.h"
- //初始化
- void SLInit(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- ps1->a = malloc(sizeof(SLDataType) * 4);
- if (ps1 == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- return;
- }
- ps1->size = 0;
- ps1->capacity = 4;
- }
- //销毁
- //把空间还给操作系统
- void SLDestroy(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- free(ps1->a);
- ps1->a = NULL;
- ps1->size = 0;
- ps1->capacity = 0;
- }
- //打印
- void SLPrint(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- int i = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", ps1->a[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- //检查容量,容量不够就扩容
- void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- if (ps1->size == ps1->capacity)
- {
- SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps1->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * ps1->capacity * 2);
- //扩上一个二倍大小的容量
- //这个数值可以自己设定,扩多了不好,扩少了也不好
- //所以扩上二倍是最合理的选择
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- return;
- }
- ps1->a = tmp;
- ps1->capacity = ps1->capacity * 2;
- }
- }
- //在中间位置(pos)插入数据
- void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps1->size);
- SLCheckCapacity(ps1);
- int end = ps1->size - 1;
- while (end >= pos)
- {
- ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];
- end--;
- }
- ps1->a[pos] = x;
- ps1->size++;
- }
- //在中间位置(pos)删除数据
- void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size);
- assert(ps1->size > 0);//可有可无
- int start = pos + 1;
- while (start <= pos + 1)
- {
- ps1->a[start - 1] = ps1->a[start];
- start++;
- }
- ps1->size--;
- }
- //尾插
- void SLPushBack(SL* ps1, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- /*SLCheckCapacity(ps1);
- ps1->a[ps1->size] = x;
- ps1->size++;*/
- SLInsert(ps1, ps1->size, x);
- }
- //头插
- void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- //SLCheckCapacity(ps1);
- 挪动数据
- //int end = ps1->size - 1;
- //while (end >= 0)
- //{
- //ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];//把数据往后挪
- //end--;
- //}
- //ps1->a[0] = x;
- //ps1->size++;
- SLInsert(ps1, 0, x);
- }
- //尾删
- void SLPopBack(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- 温柔的检查
- //if (ps1->size == 0)
- //{
- //return;
- //}
- //ps1->size--;
- //暴力的检查
- /*assert(ps1->size > 0);
- ps1->size--;*/
- SLErase(ps1, ps1->size - 1);
- }
- //头删
- void SLPopFront(SL* ps1)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- //暴力检查
- assert(ps1->size > 0);
- int start = 0;
- while (start < ps1->size - 1)
- {
- ps1->a[start] = ps1->a[start + 1];
- start++;
- }
- ps1->size--;
- //SLErase(ps1, 0);
- }
- //查找
- //找到了返回下标,找不到返回-1
- int SLFind(SL* ps1, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- int i = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++)
- {
- if (ps1->a[i] == x)
- {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- //修改
- void SLModify(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps1);
- assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size);
- ps1->a[pos] = x;
- }
SeqList.h的内容
- #pragma once
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include<assert.h>
- //动态顺序表
- typedef int SLDataType;
- typedef struct SeqList
- {
- SLDataType* a;
- int size;//存储的有效数据的个数
- int capacity;//容量
- }SL;
- //初始化
- void SLInit(SL* ps1);
- //销毁
- //把空间还给操作系统
- void SLDestroy(SL* ps1);
- //打印
- void SLPrint(SL* ps1);
- //尾插
- void SLPushBack(SL* ps1,SLDataType x);
- //尾删
- void SLPopBack(SL* ps1);
- //头插
- void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDataType x);
- //头删
- void SLPopFront(SL* ps1);
- //在中间位置(pos)插入数据
- void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDataType x);
- //在中间位置(pos)删除数据
- void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos);
- //查找
- //找到了返回下标,找不到返回-1
- int SLFind(SL* ps1, SLDataType x);
- //修改
- void SLModify(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDataType x);
-
test.c的内容
- void menu()
- {
- printf("***********************************************************\n");
- printf("1、尾插数据 2、尾删数据\n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("3、头插数据 4、头删数据\n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("5、在任意位置插入数据(位置3插入20)\n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("6、在任意位置删除数据 \n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("7、查找某个数据的位置,并删除它 \n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("8、删除顺序表中有的 某个数据 \n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("9、打印数据 \n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("-1、退出 \n");
- printf("\n");
- printf("***********************************************************\n");
-
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- printf("************* 欢迎大家来到动态顺序表的测试 **************\n");
- int option = 0;
- SL s;
- SLInit(&s);
- do
- {
- menu();
- printf("请输入你的操作:>");
- scanf_s("%d", &option);
- int sum = 0;
- int x = 0;
- int y = 0;
- int z = 0;
- int pos = 0;
- int w = 0;
- switch (option)
- {
- case 1:
- printf("请依次输入你要尾插的数据:,以-1结束\n");
- scanf_s("%d", &sum);
- while (sum != -1)
- {
- SLPushBack(&s, sum); // 1.尾插
- scanf_s("%d", &sum);
- }
- break;
- case 2:
- SLPopBack(&s); // 2.尾删
- break;
- case 3:
- scanf_s("%d", &x);
- SLPushFront(&s, x); // 3.头插
- break;
- case 4:
- SLPopFront(&s); // 4.头删
- break;
- case 5:
- SLInsert(&s, 3, 20); // 5.在任意位置插入数据
- break;
- case 6:
- SLErase(&s, 3); // 6.在任意位置删除数据
- break;
- case 7:
- printf("请输入要删除序列的中的某个数字\n");
- scanf_s("%d", &z);
- y = SLFind(&s, z); // 7.查找某个数字的位置,并且删除它
- printf("%d的位置在%d处: \n", z, y);
- if (y != -1)
- {
- SLErase(&s, y);
- }
- break;
- case 8:
- printf("请输入要删除序列的中的数字\n"); //8.删除顺序表中 所有的 某个数据
- scanf_s("%d", &w);
- pos = SLFind(&s, w, 0);
- while (pos != -1)
- {
- SLErase(&s, pos);
- pos = SLFind(&s, w, pos);
- }
- break;
- case 9:
- SLPrint(&s);
- break;
- default:
- if (option == -1)
- {
- exit(0); // 退出程序
- }
- else
- {
- printf("输入错误,请重新输入\n");
- }
- break;
-
- }
- } while (option != -1); // 退出程序
- SLDestroy(&s);
- return 0;
- }
好啦,小雅兰今天的顺序表的更新版的内容就到这里啦,继续加油刷题和学习算法噢!!!




