文章目录
- 一、实验内容
- 二、实验步骤
- 1、页面布局
- 2、数据库
- 3、登录活动
- 4、增删改查
- 三、运行演示
- 四、实验总结
- 五、源码下载
一、实验内容
根据Android数据存储的内容,综合应用SharedPreferences和SQLite数据库实现一个用户信息管理系统,强化对SharedPreferences的理解的使用,熟练掌握SQLite的操作。要求:
- 巩固Android应用开发工具(Eclipse或者AndroidStudio)的常规用法;
- 巩固Activity、UI控件的常规用法;
- 掌握SharedPpreferences数据存储的使用;
- 掌握SQLite数据库及SQLiteOpenHelper的使用。
二、实验步骤
1、页面布局
本次布局提倡从简原则,按照往常习惯,我肯定是创建多个Activity,然后每个Activity设置下页面,分别从主页面跳转到各个页面。既然是实验,那就从简,实现核心的思想就可以了,底层逻辑实现出来,表面内容那不是花时间设计下就行了。言归正传,主页面布局如下,没有任何亮点可言,比较常规,只给Button和TextView都设置了background。
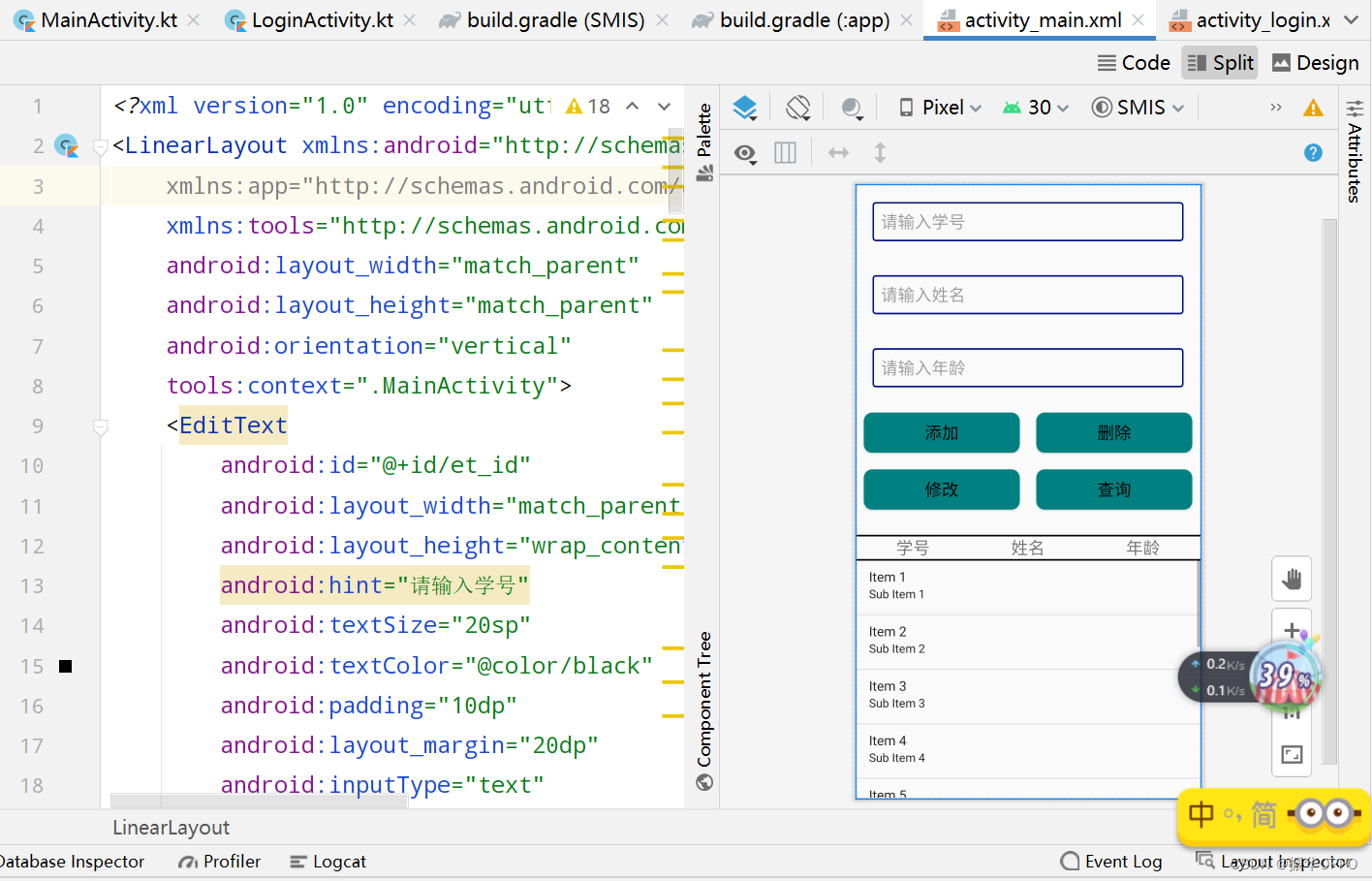
完整的layout代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入学号"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:inputType="text"
android:background="@drawable/et_selector" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入姓名"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:inputType="text"
android:background="@drawable/et_selector" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_age"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入年龄"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:inputType="text"
android:background="@drawable/et_selector" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_insert"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="添加"
android:background="@drawable/btn_selector"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_delete"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="删除"
android:background="@drawable/btn_selector"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_update"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="修改"
android:background="@drawable/btn_selector"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_query"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="查询"
android:background="@drawable/btn_selector"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="2dp"
android:background="@color/black"/>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="学号"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="姓名"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="年龄"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="2dp"
android:background="@color/black"/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv_stu"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
2、数据库
考查对SQLite的熟练程度,其实就是Android提供了一个数据库帮助类,帮我们进行数据库的各种操作。我们要做的就是建库建表,写个增删改查的方法,然后剩下的事情交给系统。这里是学生表的建表语句,一切属性都能用text表示。
private val CREATE_STUDENT = "create table Student (" +
"id text primary key," +
"name text," +
"age text)"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
再看学生类,简直封装的太好了,Kotlin的魅力所在,换做Java又是属性、构造函数、get和set方法。
class Student(val id:String, val name:String, val age:String) {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
下面看数据库的增删改查操作,所有的操作都是针对数据库的Student表来的,增加、删除和修改都很简单,使用ContentValues添加键值对。查询是最关键的,使用cursor游标一行行遍历表数据,各种约束条件可以自己加,正常全查就完事了。
val dbHelper = DBHelper(context, "stu.db", 1)
lateinit var db:SQLiteDatabase
fun openDB() {
db = dbHelper.writableDatabase
}
fun closeDB() {
if (db != null) dbHelper.close()
}
// 插入学生
fun insertStudent(stu: Student) {
val values = ContentValues().apply {
put("id", stu.id)
put("name", stu.name)
put("age", stu.age)
}
db.insert("Student", null, values)
}
// 删除学生
fun deleteStudent(stu: Student) {
db.delete("Student", "id = ?", arrayOf(stu.id))
}
// 更新学生
fun updateStudent(stu: Student) {
val values = ContentValues()
values.put("name", stu.name)
values.put("age", stu.age)
db.update("Student", values, "id = ?", arrayOf(stu.id))
}
// 查询所有学生
fun queryAllStudent():ArrayList<Student> {
val cursor = db.query("Student", null, null, null, null, null, null)
val stuList = ArrayList<Student>()
if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {
do {
val id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("id"))
val name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"))
val age = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("age"))
val stu = Student(id, name, age)
stuList.add(stu)
} while (cursor.moveToNext())
}
cursor.close()
return stuList
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
3、登录活动
登录活动用的是sharedPreferences,它使用方法非常easy,首先初始化一个sharedPreferences对象,文件名和访问类型自定义。读数据就是调用getString获取键值对,设定个默认值。写数据就是调用sharedPreferences.edit()赋值给editor对象,然后putString读取键值对。还记录了下app的使用次数。
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityLoginBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences("data", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
var editor = sharedPreferences.edit()
// 得到之前的使用次数,然后每次打开app都加1
var count = sharedPreferences.getString("count", "0");
binding.tvCount.text = (count!!.toInt() + 1).toString()
// 保存键值对到sharedpreferences中
editor.putString("count", (count!!.toInt() + 1).toString())
editor.apply()
binding.btnLogin.setOnClickListener{
editor.putString("account", binding.etAccount.toString().trim())
editor.putString("password", binding.etPassword.toString().trim())
editor.apply()
Toast.makeText(this, "登录成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
val intent = Intent(this, MainActivity::class.java)
startActivity(intent)
finish()
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
4、增删改查
其实对数据表的增删改查逻辑在StudentDao中已经封装好了,我们在Activity里面也只是调用方法实现界面和数据库的交互罢了。具体的操作逻辑如下:
输入学号、姓名和年龄后点击添加可以添加学生;输入学号点击查询可以查询学生信息,然后点击删除会删除信息,点击修改会修改输入框中的学生信息,最后如果输入的学号不存在而且你点查询了,会显示所有学生的信息,如果存在只会显示该学生的信息。
override fun onClick(p0: View?) {
var stuId = binding.etId.text.toString()
var stuName = binding.etName.text.toString()
var stuAge = binding.etAge.text.toString()
var stu = Student(stuId, stuName, stuAge)
var flag = (studentDao.queryById(stuId) != null)
when(p0?.id) {
R.id.btn_insert->{
if (flag) {
Toast.makeText(this, "学生已存在,无法添加", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
studentDao.insertStudent(stu)
Toast.makeText(this, "添加成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
R.id.btn_delete->{
if (flag) {
studentDao.deleteStudent(stu)
Toast.makeText(this, "删除成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "该学生不存在,无法删除", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
R.id.btn_update->{
if (flag) {
studentDao.updateStudent(stu)
Toast.makeText(this, "修改成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "该学生不存在,无法修改", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
R.id.btn_query->{
if (flag) {// 如果存在则补全信息
binding.etAge.setText(studentDao.queryById(stuId)?.age)
binding.etName.setText(studentDao.queryById(stuId)?.name)
Toast.makeText(this, "查询到该学生信息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {// 不存在则显示所有学生信息
studentList = studentDao.queryAllStudent()
adapter = StudentAdapter(this, R.layout.item_student, studentList)
binding.lvStu.adapter = adapter
Toast.makeText(this, "查询所有学生信息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
三、运行演示
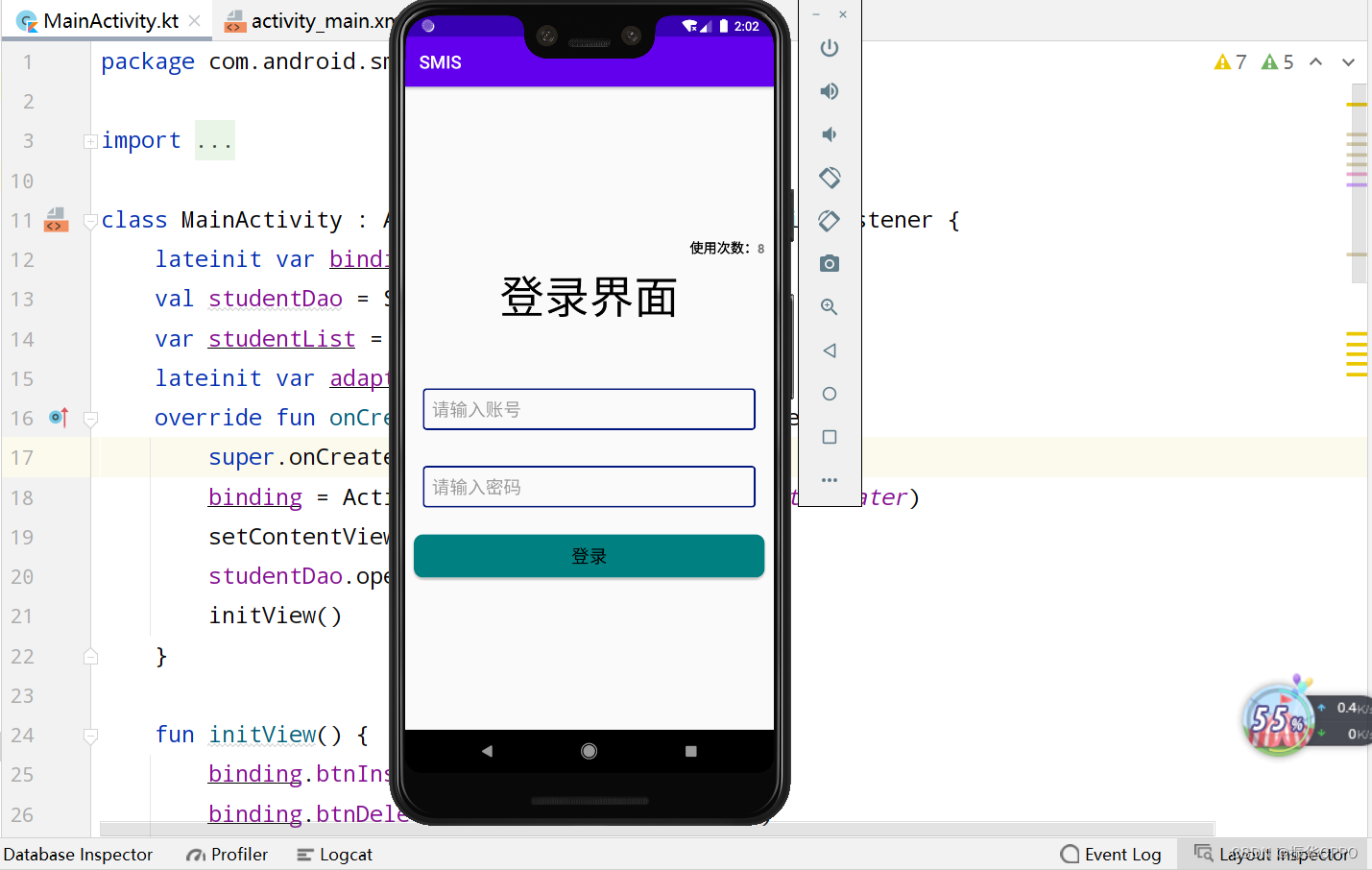
1、首先进入登录界面,输入账号和密码然后点击登录即可,右上角是使用次数。
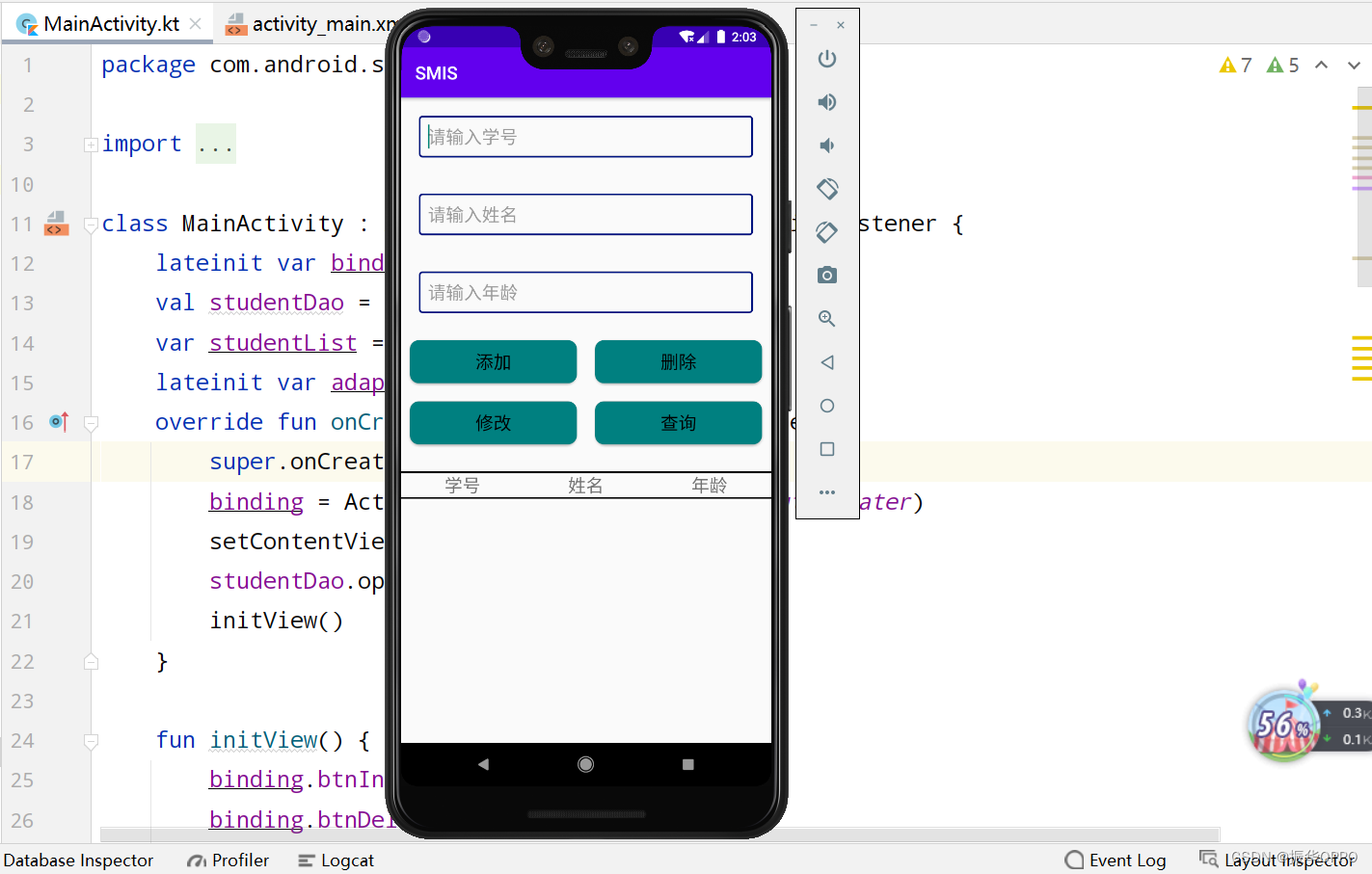
2、进入主界面,我们输入学号、姓名和年龄进行添加学生。
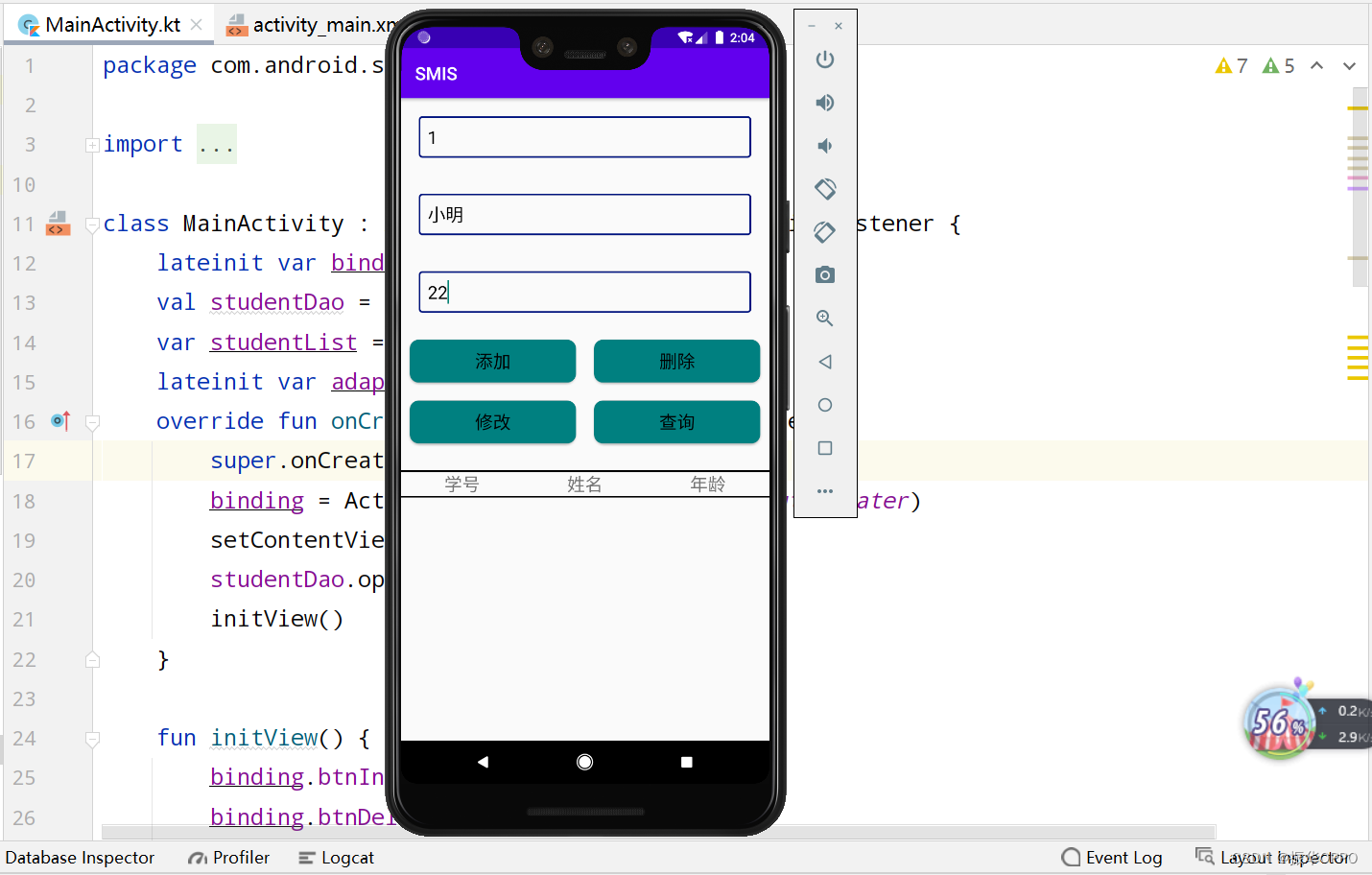
3、点击添加按钮,添加成功。再依次添加几个学生。
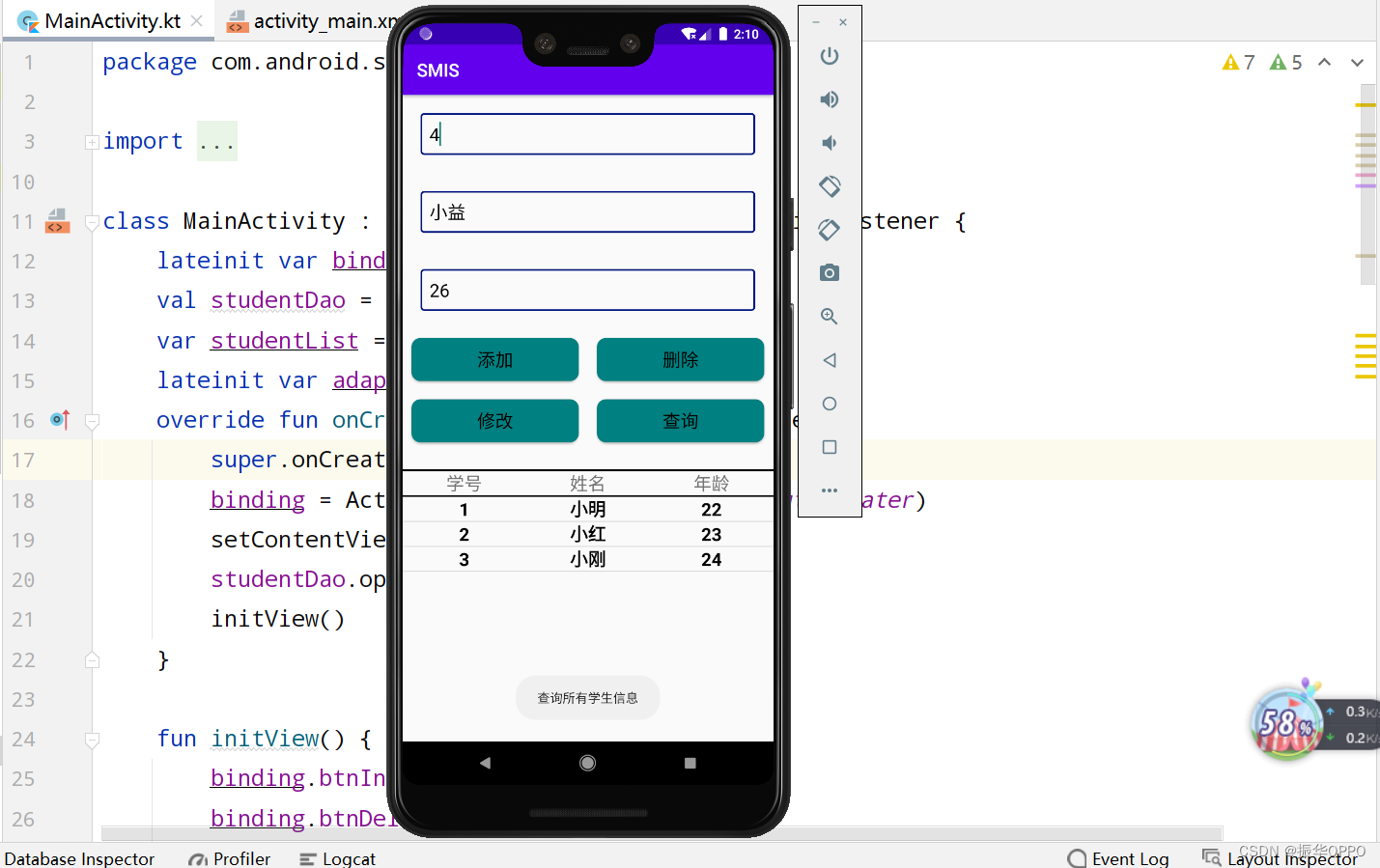
4、点击查询,此时学号是不存在的,所以就查询了所有学生的信息。
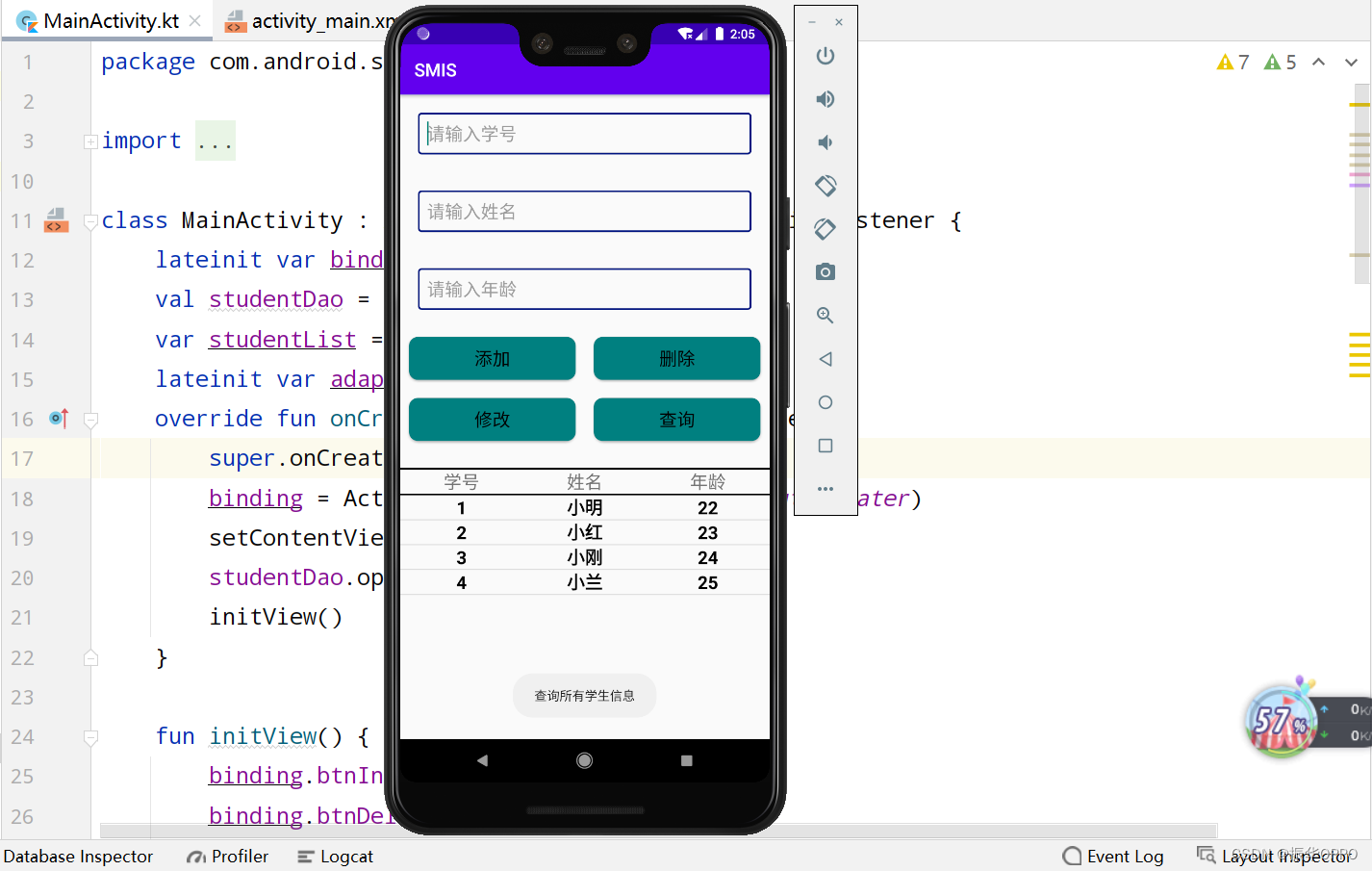
5、我们输入学号4,然后点击查询,可以看到查询到信息并自动补全了。
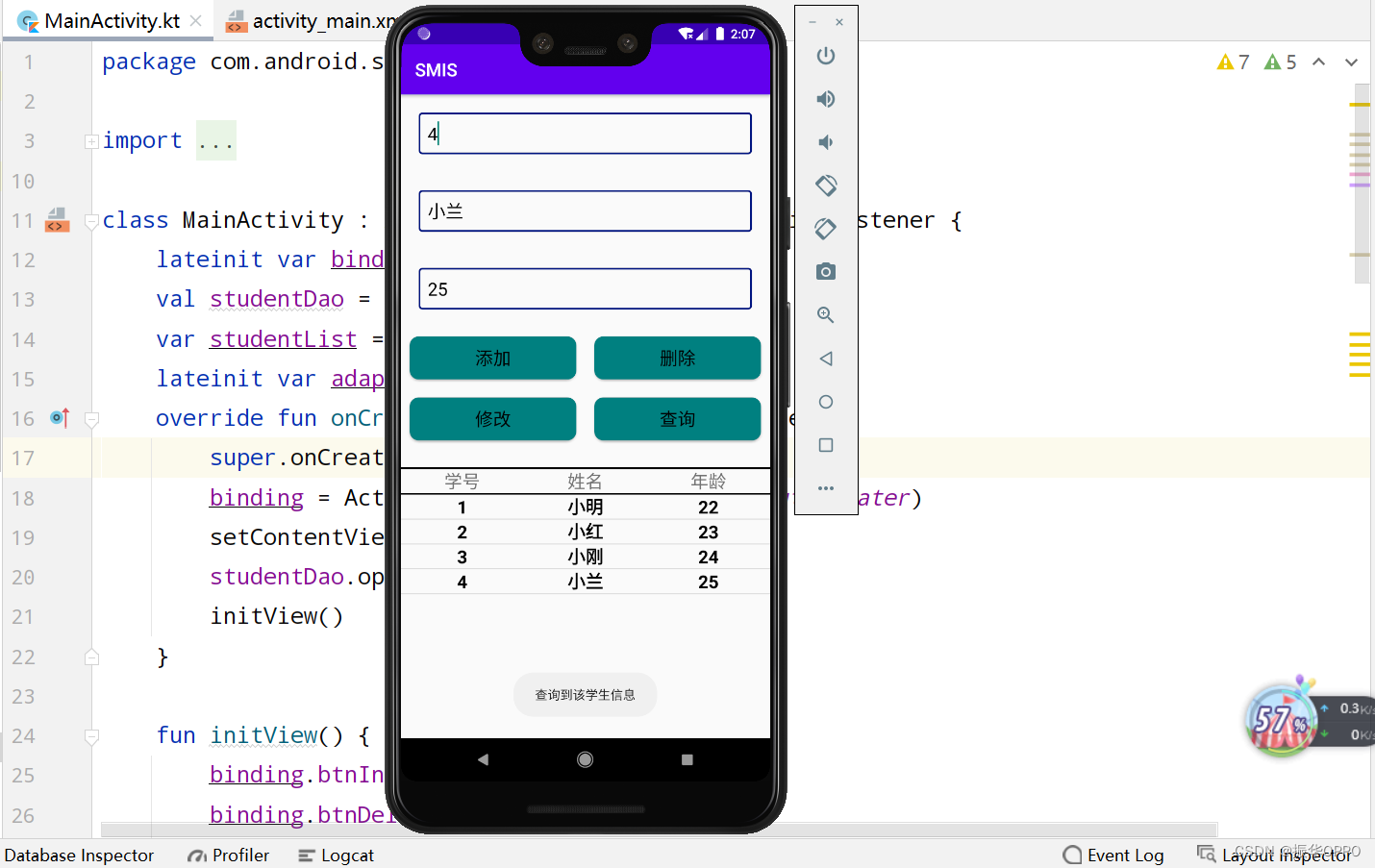
6、修改姓名和年龄,然后再点修改,再点击查询,发现已经修改好了信息。
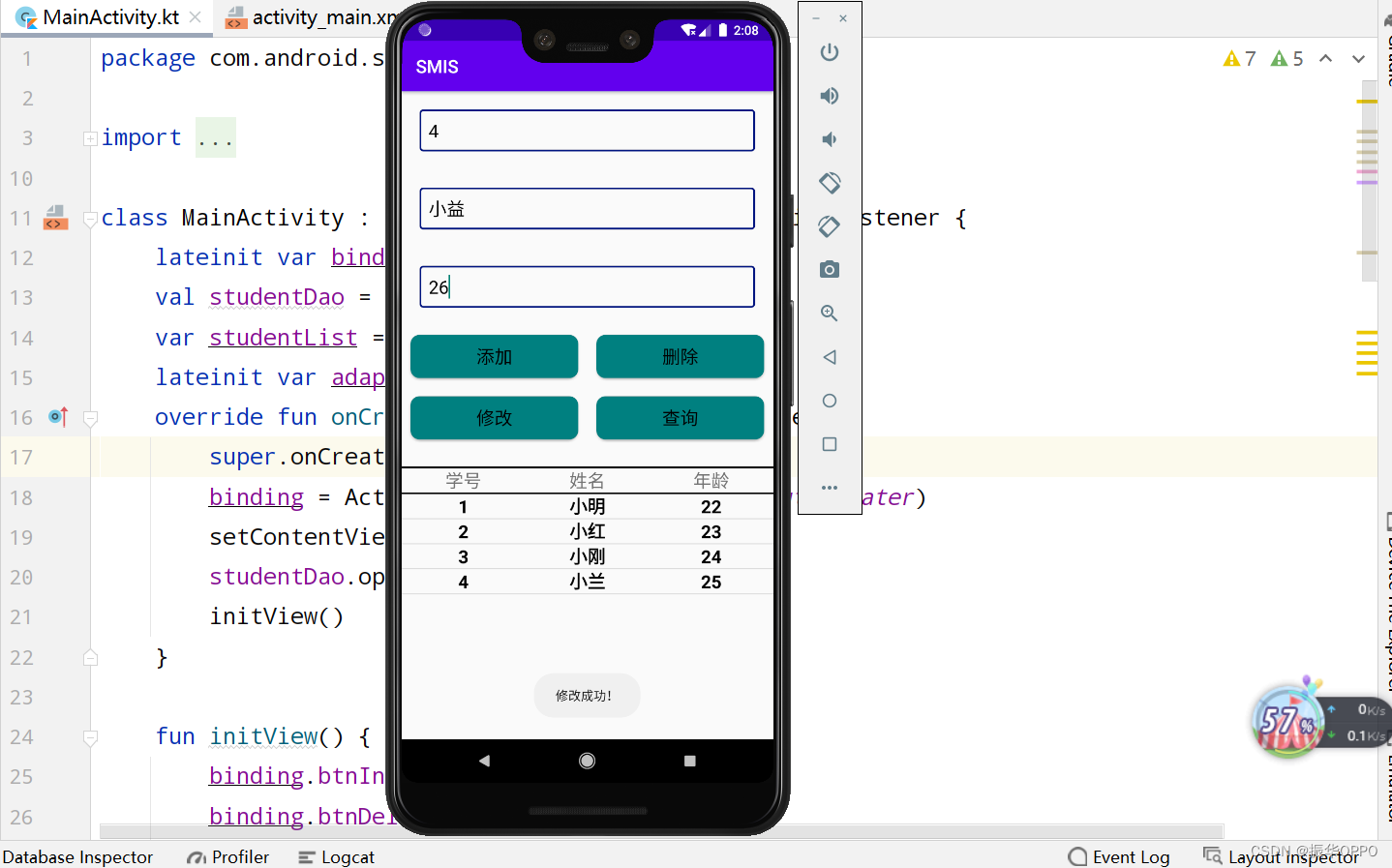
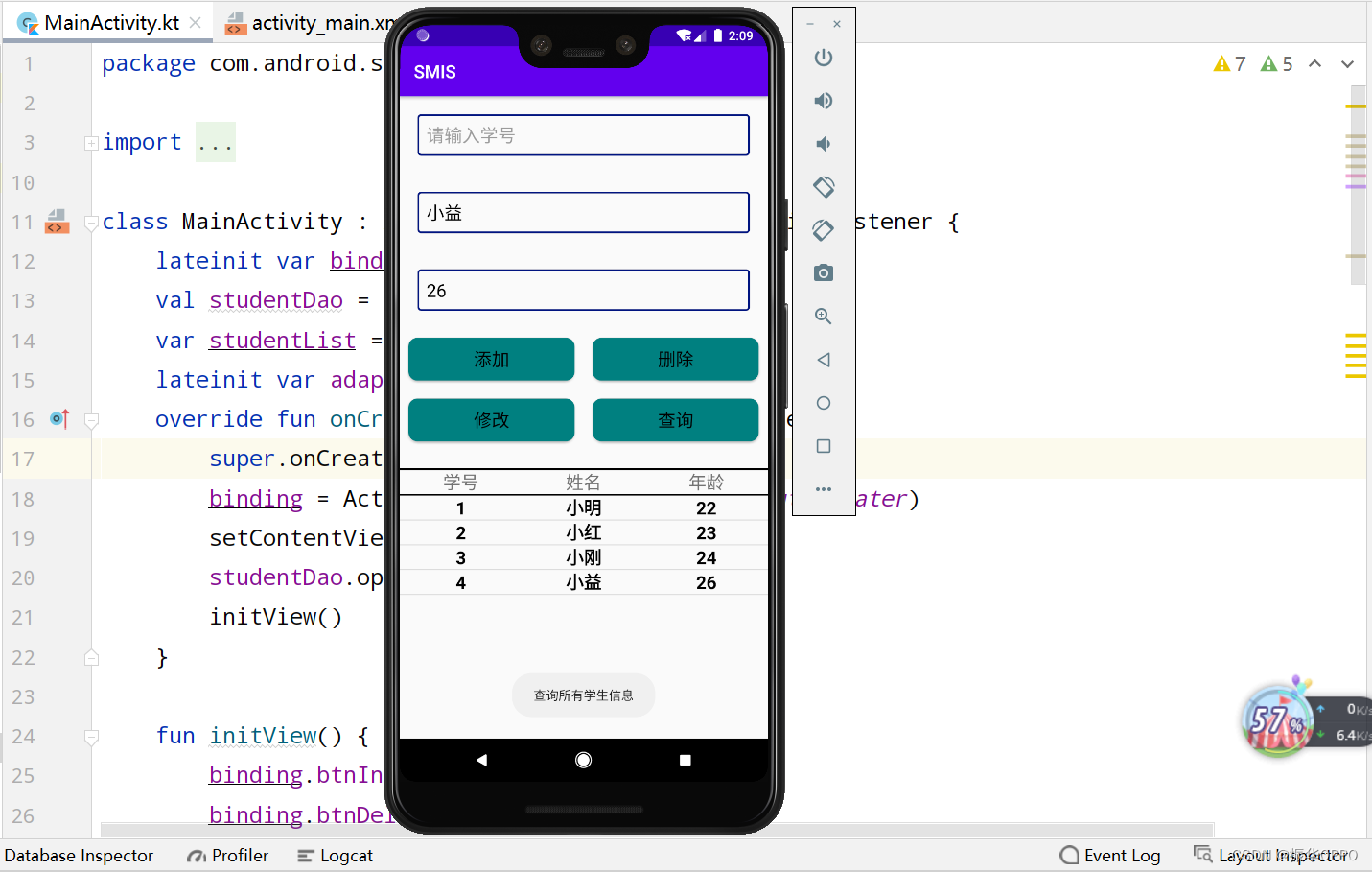
7、我们再查询小益的信息,然后删除小益的信息。
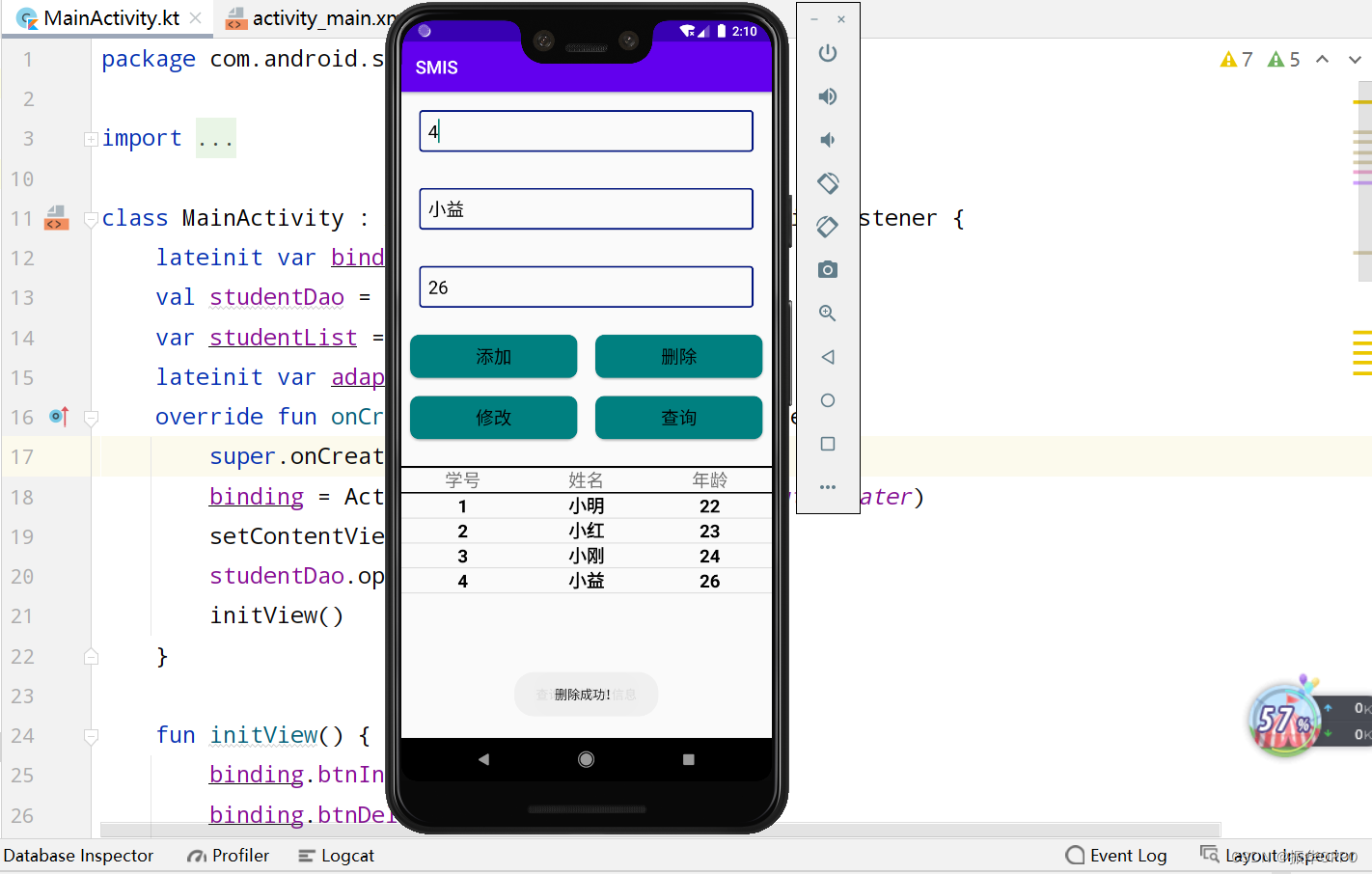
四、实验总结
其实学生系统涉及到数据库的操作完全和前面的其他系统相似,真正做起来还是比较繁琐的。哪里有什么容易代码,都是在一个个bug解决中完成的。理论引导实战,光理论只会纸上谈兵,光实践缺少方法论,基础打牢了才能进阶,不然上限不会高,基础决定了你的上限。
五、源码下载
| 源代码已上传CSDN,点击下载 |
|---|
| 源代码已上传GitHub,点击下载 |

 微信公众号
微信公众号

